Page 355 - Engineering Electromagnetics, 8th Edition
P. 355
CHAPTER 10 Transmission Lines 337
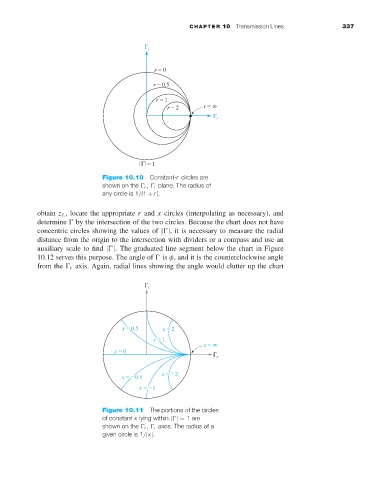
Figure 10.10 Constant-r circles are
shown on the r , i plane. The radius of
any circle is 1/(1 + r ).
obtain z L , locate the appropriate r and x circles (interpolating as necessary), and
determine by the intersection of the two circles. Because the chart does not have
concentric circles showing the values of | |,itis necessary to measure the radial
distance from the origin to the intersection with dividers or a compass and use an
auxiliary scale to find | |. The graduated line segment below the chart in Figure
10.12 serves this purpose. The angle of is φ, and it is the counterclockwise angle
from the r axis. Again, radial lines showing the angle would clutter up the chart
Figure 10.11 The portions of the circles
of constant x lying within | |= 1are
shown on the r , i axes. The radius of a
given circle is 1/|x|.