Page 460 - Enhanced Oil Recovery in Shale and Tight Reservoirs
P. 460
Air injection 427
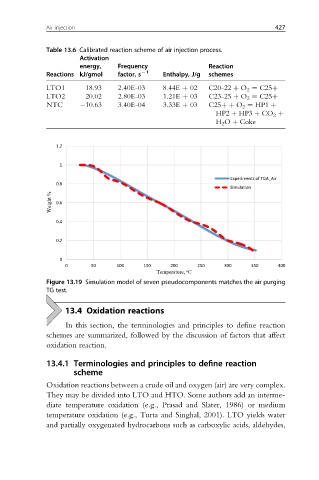
Table 13.6 Calibrated reaction scheme of air injection process.
Activation
energy, Frequency Reaction
Reactions kJ/gmol factor, s L1 Enthalpy, J/g schemes
LTO1 18.93 2.40E-03 8.44E þ 02 C20-22 þ O 2 ¼ C25þ
LTO2 20.02 2.80E-03 1.21E þ 03 C23-25 þ O 2 ¼ C25þ
NTC 10.63 3.40E-04 3.33E þ 03 C25þþ O 2 ¼ HP1 þ
HP2 þ HP3 þ CO 2 þ
H 2 O þ Coke
1.2
1
Experiments of TGA_Air
0.8
Simula on
Weight % 0.6
0.4
0.2
0
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400
o
Temperature, C
Figure 13.19 Simulation model of seven pseudocomponents matches the air purging
TG test.
13.4 Oxidation reactions
In this section, the terminologies and principles to define reaction
schemes are summarized, followed by the discussion of factors that affect
oxidation reaction.
13.4.1 Terminologies and principles to define reaction
scheme
Oxidation reactions between a crude oil and oxygen (air) are very complex.
They may be divided into LTO and HTO. Some authors add an interme-
diate temperature oxidation (e.g., Prasad and Slater, 1986) or medium
temperature oxidation (e.g., Turta and Singhal, 2001). LTO yields water
and partially oxygenated hydrocarbons such as carboxylic acids, aldehydes,