Page 235 - Facility Piping Systems Handbook for Industrial, Commercial, and Healthcare Facilities
P. 235
HEAT TRANSFER, INSULATION, AND FREEZE PROTECTION
HEAT TRANSFER, INSULATION, AND FREEZE PROTECTION 5.19
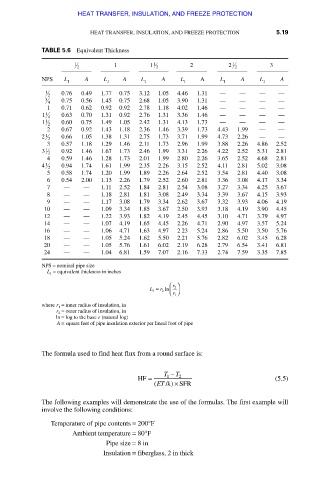
TABLE 5.6 Equivalent Thickness
1
1
1 2 1 1 2 2 2 2 3
NPS L A L A L A L 1 A L A L A
1
1
1
1
1
1 2 0.76 0.49 1.77 0.75 3.12 1.05 4.46 1.31 — — — —
3 4 0.75 0.56 1.45 0.75 2.68 1.05 3.90 1.31 — — — —
1 0.71 0.62 0.92 0.92 2.78 1.18 4.02 1.46 — — — —
1 0.63 0.70 1.31 0.92 2.76 1.31 3.36 1.46 — — — —
1 4
1
1 2 0.60 0.75 1.49 1.05 2.42 1.31 4.13 1.73 — — — —
2 0.67 0.92 1.43 1.18 2.36 1.46 3.39 1.73 4.43 1.99 — —
1
2 2 0.66 1.05 1.38 1.31 2.75 1.73 3.71 1.99 4.73 2.26 — —
3 0.57 1.18 1.29 1.46 2.11 1.73 2.96 1.99 3.88 2.26 4.86 2.52
1
3 2 0.92 1.46 1.67 1.73 2.46 1.99 3.31 2.26 4.22 2.52 5.31 2.81
4 0.59 1.46 1.28 1.73 2.01 1.99 2.80 2.26 3.65 2.52 4.68 2.81
1
4 2 0.94 1.74 1.61 1.99 2.35 2.26 3.15 2.52 4.11 2.81 5.02 3.08
5 0.58 1.74 1.20 1.99 1.89 2.26 2.64 2.52 3.54 2.81 4.40 3.08
6 0.54 2.00 1.13 2.26 1.79 2.52 2.60 2.81 3.36 3.08 4.17 3.34
7 — — 1.11 2.52 1.84 2.81 2.54 3.08 3.27 3.34 4.25 3.67
8 — — 1.18 2.81 1.81 3.08 2.49 3.34 3.39 3.67 4.15 3.93
9 — — 1.17 3.08 1.79 3.34 2.62 3.67 3.32 3.93 4.06 4.19
10 — — 1.09 3.34 1.85 3.67 2.50 3.93 3.18 4.19 3.90 4.45
12 — — 1.22 3.93 1.82 4.19 2.45 4.45 3.10 4.71 3.79 4.97
14 — — 1.07 4.19 1.65 4.45 2.26 4.71 2.90 4.97 3.57 5.24
16 — — 1.06 4.71 1.63 4.97 2 23 5.24 2.86 5.50 3.50 5.76
18 — — 1.05 5.24 1.62 5.50 2.21 5.76 2.82 6.02 3.45 6.28
20 — — 1.05 5.76 1.61 6.02 2.19 6.28 2.79 6.54 3.41 6.81
24 — — 1.04 6.81 1.59 7.07 2.16 7.33 2.74 7.59 3.35 7.85
NPS = nominal pipe size
L 1 = equivalent thickness in inches
⎛ r 2 ⎞
L 1 = r 2 ln ⎜ ⎝ r 1 ⎠ ⎟
where r 1 = inner radius of insulation, in
r 2 = outer radius of insulation, in
ln = log to the base e (natural log)
A = square feet of pipe insulation exterior per lineal foot of pipe
The formula used to find heat flux from a round surface is:
HF = T 1 − T 2 (5.5)
( ET /k) × SFR
The following examples will demonstrate the use of the formulas. The first example will
involve the following conditions:
Temperature of pipe contents = 200°F
Ambient temperature = 80°F
Pipe size = 8 in
Insulation = fiberglass, 2 in thick
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.accessengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.