Page 383 - Failure Analysis Case Studies II
P. 383
368
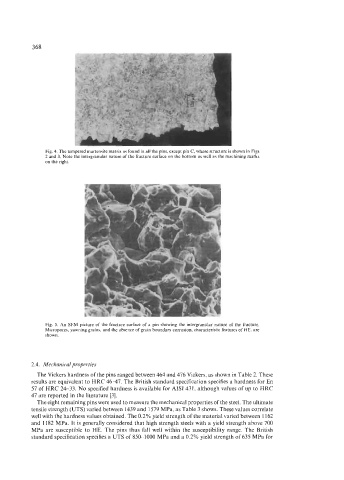
Fig. 4. The tempered martensite matrix as found in all the pins, except pin C, whose structure is shown in Figs
2 and 3. Note the intergranular nature of the fracture surface on the bottom as well as the machining marks
on the right.
Fig. 5. An SEM picture of the fracture surface of a pin showing the intergranular nature of the fracture.
Micropores, yawning grains, and the absence of grain boundary corrosion, characteristic features of HE, are
shown.
2.4. Mechanicalproperties
The Vickers hardness of the pins ranged between 464 and 476 Vickers, as shown in Table 2. These
results are equivalent to HRC 46-47. The British standard specification specifies a hardness for En
57 of HRC 24-33. No specified hardness is available for AIS1 431, although values of up to HRC
47 are reported in the literature [3].
The eight remaining pins were used to measure the mechanical properties of the steel. The ultimate
tensile strength (UTS) varied between 1439 and 1579 MPa, as Table 3 shows. These values correlate
well with the hardness values obtained. The 0.2% yield strength of the material varied between 1162
and 1182 MPa. It is generally considered that high strength steels with a yield strength above 700
MPa are susceptible to HE. The pins thus fall well within the susceptibility range. The British
standard specification specifies a UTS of 85Ck-1000 MPa and a 0.2% yield strength of 635 MPa for