Page 385 - Failure Analysis Case Studies II
P. 385
3 70
austenitizing temperatures [4]. The steel is susceptible to temper embrittlement at temperatures near
550°C.
3. DISCUSSION
The pins failed due to hydrogen embrittlement (HE). They had been heat treated into the
susceptible range for HE. HE is a mechanical/environmental failure process that results from the
absorption of hydrogen into the metal, usually in combination with stress (residual or applied) [SI.
HE is one of four types of environmental cracking [6] and is mainly a problem in high strength
steels. The susceptibility of a material increases with :
(i) The strength (e.g. hardness).
(ii) Increasing amounts of cold work.
(iii) Increasing residual and applied stress.
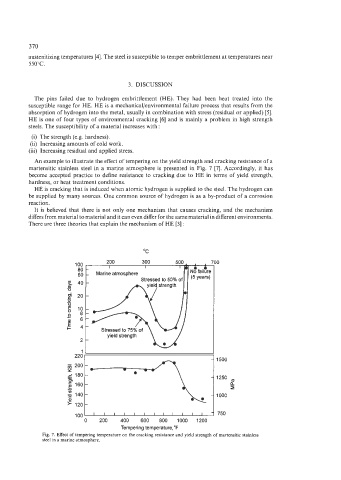
An example to illustrate the effect of tempering on the yield strength and cracking resistance of a
martensitic stainless steel in a marine atmosphere is presented in Fig. 7 [7]. Accordingly, it has
become accepted practice to define resistance to cracking due to HE in terms of yield strength,
hardness, or heat treatment conditions.
HE is cracking that is induced when atomic hydrogen is supplied to the steel. The hydrogen can
be supplied by many sources. One common source of hydrogen is as a by-product of a corrosion
reaction.
It is believed that there is not only one mechanism that causes cracking, and the mechanism
differs from material to material and it can even differ for the same material in different environments.
There are three theories that explain the mechanism of HE [3] :
OC
100
a0
60
,", 20
13
0
g 10
0 8
- E 6
F 4
2
1500
1250
%
1000
750
0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200
Tempering temperature, "F
Fig. 7. Effect of tempering temperature on the cracking resistance and yield strength of martensitic stainless
steel in a marine atmosphere.