Page 264 - Fair, Geyer, and Okun's Water and wastewater engineering : water supply and wastewater removal
P. 264
JWCL344_ch06_194-229.qxd 8/2/10 9:51 PM Page 224
224 Chapter 6 Water Distribution Systems: Components, Design, and Operation
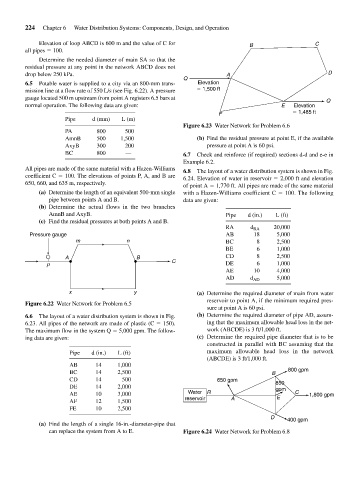
Elevation of loop ABCD is 600 m and the value of C for B C
all pipes 100.
Determine the needed diameter of main SA so that the
residual pressure at any point in the network ABCD does not
drop below 250 kPa. A D
Q
6.5 Potable water is supplied to a city via an 800-mm trans- Elevation
mission line at a flow rate of 550 L/s (see Fig. 6.22). A pressure 1,500 ft
gauge located 500 m upstream from point A registers 6.5 bars at Q
normal operation. The following data are given: E Elevation
F 1,485 ft
Pipe d (mm) L (m)
Figure 6.23 Water Network for Problem 6.6
PA 800 500
AmnB 500 1,500 (b) Find the residual pressure at point E, if the available
AxyB 300 200 pressure at point A is 60 psi.
BC 800 — 6.7 Check and reinforce (if required) sections d-d and e-e in
Example 6.2.
All pipes are made of the same material with a Hazen-Williams 6.8 The layout of a water distribution system is shown in Fig.
coefficient C 100. The elevations of points P, A, and B are 6.24. Elevation of water in reservoir 2,000 ft and elevation
650, 660, and 635 m, respectively.
of point A 1,770 ft. All pipes are made of the same material
(a) Determine the length of an equivalent 500-mm single with a Hazen-Williams coefficient C 100. The following
pipe between points A and B. data are given:
(b) Determine the actual flows in the two branches
AmnB and AxyB. Pipe d (in.) L (ft)
(c) Find the residual pressures at both points A and B.
RA d RA 20,000
Pressure gauge AB 18 5,000
m n BC 8 2,500
BE 6 1,000
A B CD 8 2,500
C
P DE 6 1,000
AE 10 4,000
AD d AD 5,000
x y (a) Determine the required diameter of main from water
reservoir to point A, if the minimum required pres-
Figure 6.22 Water Network for Problem 6.5
sure at point A is 60 psi.
6.6 The layout of a water distribution system is shown in Fig. (b) Determine the required diameter of pipe AD, assum-
6.23. All pipes of the network are made of plastic (C 150). ing that the maximum allowable head loss in the net-
The maximum flow in the system Q 5,000 gpm. The follow- work (ABCDE) is 3 ft/1,000 ft.
ing data are given: (c) Determine the required pipe diameter that is to be
constructed in parallel with BC assuming that the
Pipe d (in.) L (ft) maximum allowable head loss in the network
(ABCDE) is 3 ft/1,000 ft.
AB 14 1,000
800 gpm
BC 14 2,500 B
CD 14 500 650 gpm
850
DE 14 2,000 gpm
AE 10 3,000 Water R E C 1,800 gpm
AF 12 1,500 reservoir A
FE 10 2,500
D
400 gpm
(a) Find the length of a single 16-in.-diameter-pipe that
can replace the system from A to E. Figure 6.24 Water Network for Problem 6.8