Page 303 - Fair, Geyer, and Okun's Water and wastewater engineering : water supply and wastewater removal
P. 303
JWCL344_ch07_230-264.qxd 8/2/10 8:44 PM Page 263
Problems/Questions 263
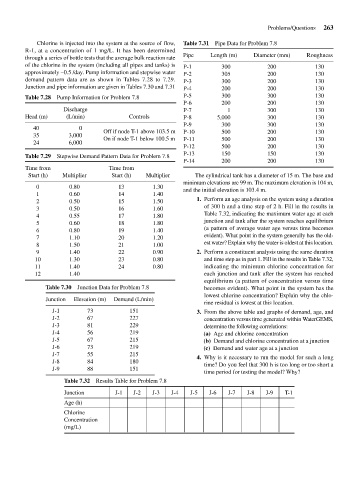
Chlorine is injected into the system at the source of flow, Table 7.31 Pipe Data for Problem 7.8
R-1, at a concentration of 1 mg/L. It has been determined
through a series of bottle tests that the average bulk reaction rate Pipe Length (m) Diameter (mm) Roughness
of the chlorine in the system (including all pipes and tanks) is P-1 300 200 130
approximately –0.5 /day. Pump information and stepwise water P-2 305 200 130
demand pattern data are as shown in Tables 7.28 to 7.29. P-3 300 200 130
Junction and pipe information are given in Tables 7.30 and 7.31 P-4 200 200 130
Table 7.28 Pump Information for Problem 7.8 P-5 300 300 130
P-6 200 200 130
Discharge P-7 1 300 130
Head (m) (L/min) Controls P-8 5,000 300 130
P-9 300 300 130
40 0
Off if node T-1 above 103.5 m P-10 500 200 130
35 3,000
On if node T-1 below 100.5 m P-11 500 200 130
24 6,000
P-12 500 200 130
Table 7.29 Stepwise Demand Pattern Data for Problem 7.8 P-13 150 150 130
P-14 200 200 130
Time from Time from
Start (h) Multiplier Start (h) Multiplier The cylindrical tank has a diameter of 15 m. The base and
minimum elevations are 99 m. The maximum elevation is 104 m,
0 0.80 13 1.30
and the initial elevation is 103.4 m.
1 0.60 14 1.40
2 0.50 15 1.50 1. Perform an age analysis on the system using a duration
3 0.50 16 1.60 of 300 h and a time step of 2 h. Fill in the results in
4 0.55 17 1.80 Table 7.32, indicating the maximum water age at each
5 0.60 18 1.80 junction and tank after the system reaches equilibrium
6 0.80 19 1.40 (a pattern of average water age versus time becomes
7 1.10 20 1.20 evident). What point in the system generally has the old-
8 1.50 21 1.00 est water? Explain why the water is oldest at this location.
9 1.40 22 0.90 2. Perform a constituent analysis using the same duration
10 1.30 23 0.80 and time step as in part 1. Fill in the results in Table 7.32,
11 1.40 24 0.80 indicating the minimum chlorine concentration for
12 1.40 each junction and tank after the system has reached
equilibrium (a pattern of concentration versus time
Table 7.30 Junction Data for Problem 7.8 becomes evident). What point in the system has the
lowest chlorine concentration? Explain why the chlo-
Junction Elevation (m) Demand (L/min)
rine residual is lowest at this location.
J-1 73 151 3. From the above table and graphs of demand, age, and
J-2 67 227 concentration versus time generated within WaterGEMS,
J-3 81 229 determine the following correlations:
J-4 56 219 (a) Age and chlorine concentration
J-5 67 215 (b) Demand and chlorine concentration at a junction
J-6 73 219 (c) Demand and water age at a junction
J-7 55 215
4. Why is it necessary to run the model for such a long
J-8 84 180
time? Do you feel that 300 h is too long or too short a
J-9 88 151
time period for testing the model? Why?
Table 7.32 Results Table for Problem 7.8
Junction J-1 J-2 J-3 J-4 J-5 J-6 J-7 J-8 J-9 T-1
Age (h)
Chlorine
Concentration
(mg/L)