Page 432 - Fair, Geyer, and Okun's Water and wastewater engineering : water supply and wastewater removal
P. 432
JWCL344_ch11_357-397.qxd 8/2/10 9:01 PM Page 392
392 Chapter 11 Hydrology: Rainfall and Runoff
4,000
1.2 in.
Surface runoff from rain A
Rain Total area under curve A
Rate of flow, ft 3 /s 2,000 Surface Surface runoff from rain B
Total area under curve B
runoff
y A
Base rate
y
Groundwater runoff B
0
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Duration
Time units
(a) (b)
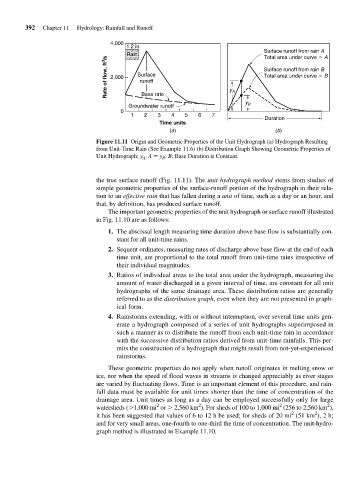
Figure 11.11 Origin and Geometric Properties of the Unit Hydrograph (a) Hydrograph Resulting
from Unit-Time Rain (See Example 11.6) (b) Distribution Graph Showing Geometric Properties of
Unit Hydrograph; y A: A y B : B; Base Duration is Constant.
the true surface runoff (Fig. 11.11). The unit-hydrograph method stems from studies of
simple geometric properties of the surface-runoff portion of the hydrograph in their rela-
tion to an effective rain that has fallen during a unit of time, such as a day or an hour, and
that, by definition, has produced surface runoff.
The important geometric properties of the unit hydrograph or surface runoff illustrated
in Fig. 11.10 are as follows:
1. The abscissal length measuring time duration above base flow is substantially con-
stant for all unit-time rains.
2. Sequent ordinates, measuring rates of discharge above base flow at the end of each
time unit, are proportional to the total runoff from unit-time rains irrespective of
their individual magnitudes.
3. Ratios of individual areas to the total area under the hydrograph, measuring the
amount of water discharged in a given interval of time, are constant for all unit
hydrographs of the same drainage area. These distribution ratios are generally
referred to as the distribution graph, even when they are not presented in graph-
ical form.
4. Rainstorms extending, with or without interruption, over several time units gen-
erate a hydrograph composed of a series of unit hydrographs superimposed in
such a manner as to distribute the runoff from each unit-time rain in accordance
with the successive distribution ratios derived from unit-time rainfalls. This per-
mits the construction of a hydrograph that might result from not-yet-experienced
rainstorms.
These geometric properties do not apply when runoff originates in melting snow or
ice, nor when the speed of flood waves in streams is changed appreciably as river stages
are varied by fluctuating flows. Time is an important element of this procedure, and rain-
fall data must be available for unit times shorter than the time of concentration of the
drainage area. Unit times as long as a day can be employed successfully only for large
2
2
2
2
watersheds ( 1,000 mi or 2,560 km ). For sheds of 100 to 1,000 mi (256 to 2,560 km ),
2
2
it has been suggested that values of 6 to 12 h be used; for sheds of 20 mi (51 km ), 2 h;
and for very small areas, one-fourth to one-third the time of concentration. The unit-hydro-
graph method is illustrated in Example 11.10.