Page 293 - Fiber Fracture
P. 293
FRACTURE OF HIGHLY ORIENTED, CHAIN-EXTENDED POLYMER FIBRES 275
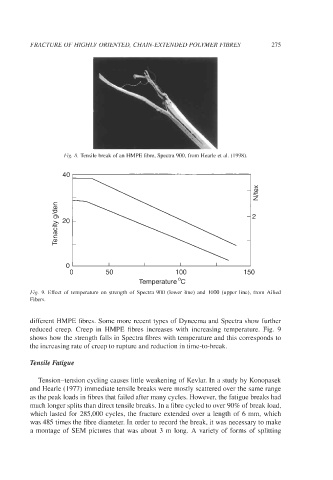
Fig. 8. Tensile break of an HMPE fibre, Spectra 900, from Hearle et al. (1998).
X
-a,
e
z
-2
0
(ZI
C
P - -
0 I I I I
different HMPE fibres. Some more recent types of Dyneema and Spectra show further
reduced creep. Creep in HMPE fibres increases with increasing temperature. Fig. 9
shows how the strength falls in Spectra fibres with temperature and this corresponds to
the increasing rate of creep to rupture and reduction in time-to-break.
Tensile Fatigue
Tension-tension cycling causes little weakening of Kevlar. In a study by Konopasek
and Hearle (1977) immediate tensile breaks were mostly scattered over the same range
as the peak loads in fibres that failed after many cycles. However, the fatigue breaks had
much longer splits than direct tensile breaks. In a fibre cycled to over 90% of break load,
which lasted for 285,000 cycles, the fracture extended over a length of 6 mm, which
was 485 times the fibre diameter. In order to record the break, it was necessary to make
a montage of SEM pictures that was about 3 m long. A variety of forms of splitting