Page 345 - Finite Element Modeling and Simulations with ANSYS Workbench
P. 345
330 Finite Element Modeling and Simulation with ANSYS Workbench
9.5 Summary
In this chapter, we discussed the governing equations for heat conduction problems and
the FEA formulation. Thermal stresses due to changes of temperatures in structures are
also discussed and the effects of constraints of the structures on the thermal stresses are
emphasized.
9.6 Review of Learning Objectives
Now that you have finished this chapter you should be able to
1. Understand the FE formulations for heat conduction and thermal stress analysis
2. Conduct heat conduction analysis of structures using FEA
3. Conduct thermal stress analysis of structures using FEA
4. Perform heat conduction and thermal stress analysis using ANSYS Workbench
PROBLEMS
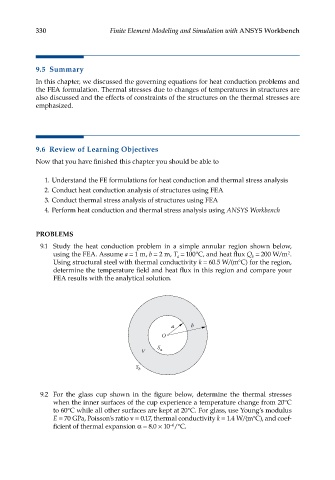
9.1 Study the heat conduction problem in a simple annular region shown below,
using the FEA. Assume a = 1 m, b = 2 m, T = 100°C, and heat flux Q = 200 W/m .
2
b
a
Using structural steel with thermal conductivity k = 60.5 W/(m°C) for the region,
determine the temperature field and heat flux in this region and compare your
FEA results with the analytical solution.
a b
O
S
V a
S b
9.2 For the glass cup shown in the figure below, determine the thermal stresses
when the inner surfaces of the cup experience a temperature change from 20°C
to 60°C while all other surfaces are kept at 20°C. For glass, use Young’s modulus
E = 70 GPa, Poisson’s ratio ν = 0.17, thermal conductivity k = 1.4 W/(m°C), and coef-
ficient of thermal expansion α = 8.0 × 10 /°C.
−6