Page 349 - Finite Element Modeling and Simulations with ANSYS Workbench
P. 349
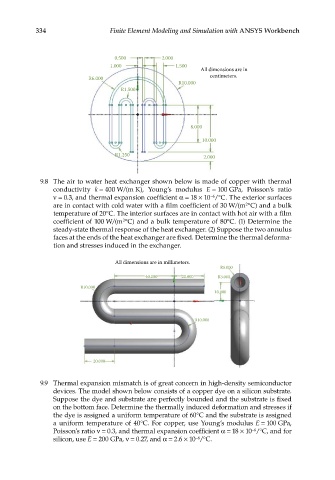
334 Finite Element Modeling and Simulation with ANSYS Workbench
0.500 2.000
1.000 1.500
All dimensions are in
centimeters.
R6.000
R10.000
R1.500
8.000
10.000
R1.250 2.000
9.8 The air to water heat exchanger shown below is made of copper with thermal
conductivity k = 400 W/(m K), Young’s modulus E = 100 GPa, Poisson’s ratio
ν = 0.3, and thermal expansion coefficient α = 18 × 10 /°C. The exterior surfaces
−6
are in contact with cold water with a film coefficient of 30 W/(m °C) and a bulk
2
temperature of 20°C. The interior surfaces are in contact with hot air with a film
coefficient of 100 W/(m °C) and a bulk temperature of 80°C. (1) Determine the
2
steady-state thermal response of the heat exchanger. (2) Suppose the two annulus
faces at the ends of the heat exchanger are fixed. Determine the thermal deforma-
tion and stresses induced in the exchanger.
All dimensions are in millimeters.
R5.000
40.000 20.000 R3.000
R10.000
10.000
R10.000
20.000
9.9 Thermal expansion mismatch is of great concern in high-density semiconductor
devices. The model shown below consists of a copper dye on a silicon substrate.
Suppose the dye and substrate are perfectly bounded and the substrate is fixed
on the bottom face. Determine the thermally induced deformation and stresses if
the dye is assigned a uniform temperature of 60°C and the substrate is assigned
a uniform temperature of 40°C. For copper, use Young’s modulus E = 100 GPa,
−6
Poisson’s ratio ν = 0.3, and thermal expansion coefficient α = 18 × 10 /°C, and for
silicon, use E = 200 GPa, ν = 0.27, and α = 2.6 × 10 /°C.
−6