Page 137 - Flexible Robotics in Medicine
P. 137
Modular origami joint operator to create bendable motions with multiple radii 123
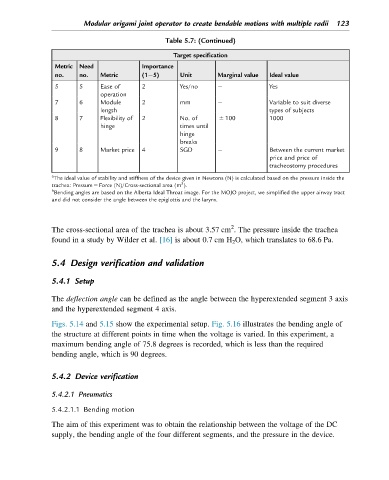
Table 5.7: (Continued)
Target specification
Metric Need Importance
no. no. Metric (1 5) Unit Marginal value Ideal value
5 5 Ease of 2 Yes/no Yes
operation
7 6 Module 2 mm Variable to suit diverse
length types of subjects
8 7 Flexibility of 2 No. of 6 100 1000
hinge times until
hinge
breaks
9 8 Market price 4 SGD Between the current market
price and price of
tracheostomy procedures
a
The ideal value of stability and stiffness of the device given in Newtons (N) is calculated based on the pressure inside the
2
trachea: Pressure 5 Force (N)/Cross-sectional area (m ).
b
Bending angles are based on the Alberta Ideal Throat image. For the MOJO project, we simplified the upper airway tract
and did not consider the angle between the epiglottis and the larynx.
2
The cross-sectional area of the trachea is about 3.57 cm . The pressure inside the trachea
found in a study by Wilder et al. [16] is about 0.7 cm H 2 O, which translates to 68.6 Pa.
5.4 Design verification and validation
5.4.1 Setup
The deflection angle can be defined as the angle between the hyperextended segment 3 axis
and the hyperextended segment 4 axis.
Figs. 5.14 and 5.15 show the experimental setup. Fig. 5.16 illustrates the bending angle of
the structure at different points in time when the voltage is varied. In this experiment, a
maximum bending angle of 75.8 degrees is recorded, which is less than the required
bending angle, which is 90 degrees.
5.4.2 Device verification
5.4.2.1 Pneumatics
5.4.2.1.1 Bending motion
The aim of this experiment was to obtain the relationship between the voltage of the DC
supply, the bending angle of the four different segments, and the pressure in the device.