Page 476 - Flexible Robotics in Medicine
P. 476
470 Chapter 20
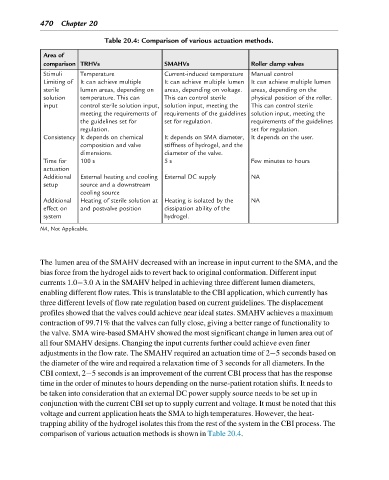
Table 20.4: Comparison of various actuation methods.
Area of
comparison TRHVs SMAHVs Roller clamp valves
Stimuli Temperature Current-induced temperature Manual control
Limiting of It can achieve multiple It can achieve multiple lumen It can achieve multiple lumen
sterile lumen areas, depending on areas, depending on voltage. areas, depending on the
solution temperature. This can This can control sterile physical position of the roller.
input control sterile solution input, solution input, meeting the This can control sterile
meeting the requirements of requirements of the guidelines solution input, meeting the
the guidelines set for set for regulation. requirements of the guidelines
regulation. set for regulation.
Consistency It depends on chemical It depends on SMA diameter, It depends on the user.
composition and valve stiffness of hydrogel, and the
dimensions. diameter of the valve.
Time for 100 s 5 s Few minutes to hours
actuation
Additional External heating and cooling External DC supply NA
setup source and a downstream
cooling source
Additional Heating of sterile solution at Heating is isolated by the NA
effect on and postvalve position dissipation ability of the
system hydrogel.
NA, Not Applicable.
The lumen area of the SMAHV decreased with an increase in input current to the SMA, and the
bias force from the hydrogel aids to revert back to original conformation. Different input
currents 1.0 3.0 A in the SMAHV helped in achieving three different lumen diameters,
enabling different flow rates. This is translatable to the CBI application, which currently has
three different levels of flow rate regulation based on current guidelines. The displacement
profiles showed that the valves could achieve near ideal states. SMAHV achieves a maximum
contraction of 99.71% that the valves can fully close, giving a better range of functionality to
the valve. SMA wire-based SMAHV showed the most significant change in lumen area out of
all four SMAHV designs. Changing the input currents further could achieve even finer
adjustments in the flow rate. The SMAHV required an actuation time of 2 5 seconds based on
the diameter of the wire and required a relaxation time of 3 seconds for all diameters. In the
CBI context, 2 5 seconds is an improvement of the current CBI process that has the response
time in the order of minutes to hours depending on the nurse-patient rotation shifts. It needs to
be taken into consideration that an external DC power supply source needs to be set up in
conjunction with the current CBI set up to supply current and voltage. It must be noted that this
voltage and current application heats the SMA to high temperatures. However, the heat-
trapping ability of the hydrogel isolates this from the rest of the system in the CBI process. The
comparison of various actuation methods is shown in Table 20.4.