Page 485 - Flexible Robotics in Medicine
P. 485
OmniFlex: omnidirectional flexible hand-held endoscopic manipulator with spheroidal joint 479
the whole prototype to reach the target region. This simplifies the actuation process, making
it easier to perform biopsies. Flexible endoscopic manipulators can be classified as
continuum and segmented. OmniFlex falls under the category of continuum endoscopic
manipulator, as no segmented joints are used (Fig. 21.1).
There are different flexion mechanisms employed in the existing endoscopic manipulators.
Such mechanisms include cable-driven and pressure-driven deflection. The focus will be
placed on cable-driven endoscopic manipulators, as it is the mechanism used in our
prototype. In cable-driven endoscopic manipulators, the force exerted on a cable at the
proximal end leads to the deflection of that cable in the distal end, resulting in a bending
motion of the shaft. To date, there are not many flexible endoscopic manipulators available.
Table 21.2: Comparison with OmniFlex, including commercially available Olympus Corporation,
Karl Storz, and Pentax Medical.
Olympus (BF- Karl Storz Pentax (EE-
Features Unit OmniFlex 3C40) (11900AP) 1580K)
Degrees of freedom High degrees of 2 (single-axis 2 (single-axis 2 (single-axis
freedom; rotation) rotation) rotation)
Omnidirectional
Angulation Degrees Upper angulation: 150 Upper Upper Upper
Lower angulation: 180 angulation: angulation: angulation:
Left angulation: 185 180 180 210
Right angulation: 195 Lower Lower Lower
Average: 170 angulation: angulation: angulation:
Range of motion 130 100 120
about any plane: 340 Total range: Total range: Total range:
310 280 330
Active control Yes/No Yes Yes Yes Yes
Hands required to Persons 1 1 1 1
operate prototype
Diameter of mm 3 3.3 6.2 5.1
manipulator
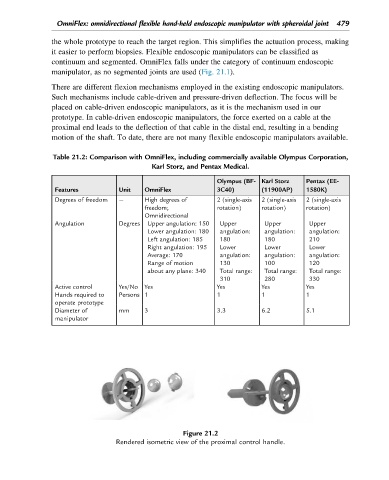
Figure 21.2
Rendered isometric view of the proximal control handle.