Page 160 - Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics of Turbomachinery
P. 160
Axial-flow Compressors and Fans 141
relative velocity in the rotor and the absolute velocity in the stator are diffused. It
will be shown later in this chapter, that the relative amount of diffusion of kinetic
energy in the rotor and stator rows, significantly influences the stage efficiency.
Thermodynamics of the compressor stage
The specific work done by the rotor on the fluid, from the steady flow energy
equation (assuming adiabatic flow) and momentum equation is
c y1 /. (5.1)
W D P W p / Pm D h 02 h 01 D U.c y2
1
2
In Chapter 4 it was proved for all axial turbomachines that h 0rel D h C w is
2
constant in the rotor. Thus,
1
2
2
1
h 1 C w D h 2 C w . (5.2)
2 1 2 2
This is a valid result as long as there is no radial shift of the streamlines across the
rotor (i.e. U 1 D U 2 ).
Across the stator, h 0 is constant, and
1 2
1 2
h 2 C c D h 3 C c . (5.3)
2 2 2 3
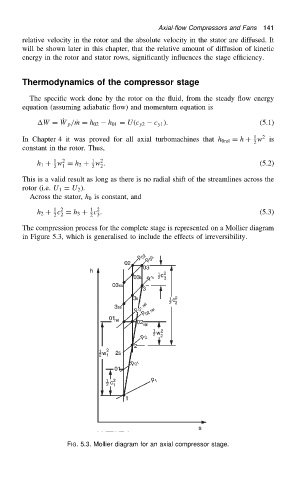
The compression process for the complete stage is represented on a Mollier diagram
in Figure 5.3, which is generalised to include the effects of irreversibility.
FIG. 5.3. Mollier diagram for an axial compressor stage.