Page 166 - Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics of Turbomachinery
P. 166
Axial-flow Compressors and Fans 147
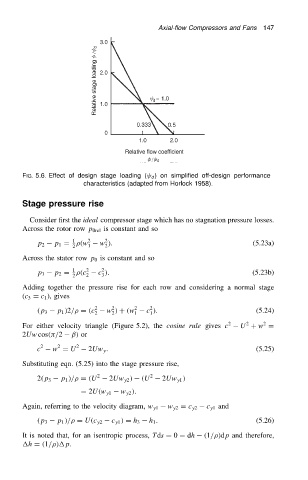
FIG. 5.6. Effect of design stage loading ( d ) on simplified off-design performance
characteristics (adapted from Horlock 1958).
Stage pressure rise
Consider first the ideal compressor stage which has no stagnation pressure losses.
Across the rotor row p 0rel is constant and so
2
1
p 1 D .w 2 w /. (5.23a)
p 2 1 2
2
Across the stator row p 0 is constant and so
2
1
p 2 D .c 2 c /. (5.23b)
p 3 2 3
2
Adding together the pressure rise for each row and considering a normal stage
(c 3 D c 1 ), gives
2
2
.p 3 p 1 /2/ D .c 2 w / C .w 2 c /. (5.24)
2 2 1 1
2
2
For either velocity triangle (Figure 5.2), the cosine rule gives c 2 U C w D
2Uw cos. /2 ˇ/ or
2
c 2 w D U 2 2Uw y . (5.25)
Substituting eqn. (5.25) into the stage pressure rise,
2.p 3 p 1 // D .U 2 2Uw y2 / .U 2 2Uw y1 /
D 2U.w y1 w y2 /.
c y1 and
Again, referring to the velocity diagram, w y1 w y2 D c y2
.p 3 p 1 // D U.c y2 c y1 / D h 3 h 1 . (5.26)
It is noted that, for an isentropic process, Tds D 0 D dh .1/ /dp and therefore,
h D .1/ /p.