Page 477 - Fluid-Structure Interactions Slender Structure and Axial Flow (Volume 1)
P. 477
/
448 SLENDER STRUCTURES AND AXIAL FLOW
24 I *-*-*- (4
I
20
"
0 1 2 30 1 2 3
Dimensionless flow velocity, U*
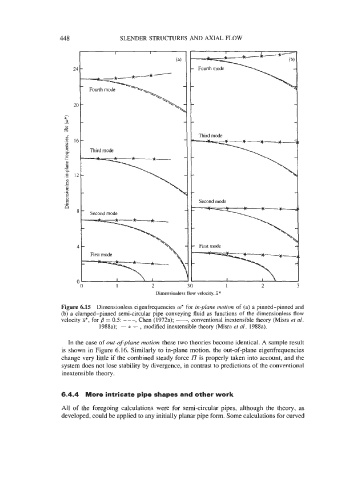
Figure 6.15 Dimensionless eigenfrequencies w* for in-plane motion of (a) a pinned-pinned and
(b) a clamped-pinned semi-circular pipe conveying fluid as functions of the dimensionless flow
velocity E*, for B = 0.5: - - -, Chen (1972a); -, conventional inextensible theory (Misra et al.
1988a); - * - , modified inextensible theory (Misra et al. 1988a).
In the case of out-of-plane motion these two theories become identical. A sample result
is shown in Figure 6.16. Similarly to in-plane motion, the out-of-plane eigenfrequencies
change very little if the combined steady force l7 is properly taken into account, and the
system does not lose stability by divergence, in contrast to predictions of the conventional
inextensible theory.
6.4.4 More intricate pipe shapes and other work
All of the foregoing calculations were for semi-circular pipes, although the theory, as
developed, could be applied to any initially planar pipe form. Some calculations for curved