Page 161 - Fluid mechanics, heat transfer, and mass transfer
P. 161
PUMPS 139
& These pumps are often installed into deep well water & No moving parts in the well. Compressor is located
applications. on top/surface.
& The impellers are commonly mixed flow types, & Airlift pumps serve two functions. First, they can
where one stage feeds the next stage through a bell eliminate fluid stratification in largeunagitated tanks.
shaped vertical diffuser. Second, they can lift a liquid above its normal surface
. What type of application a turbine pump is suitable? elevation without dilution and without introducing
shear that damages fragile suspended solids.
& For low flow rates of low-viscosity liquids requiring
high delivery pressures than normal centrifugal & Gas-lift pumps are used to lift oil from oil wells.
pumps. & Its construction consists of a vertical pipe, open on
. What type of flow patterns are obtainable for turbine both ends, that serves as a fluid pipe. A separate,
pumps? smaller line, extends to the bottom of the fluid pipe
and makes a U-turn. The open end extends a short
& Mixed flow: Partly radial (centrifugal) and partly
distance into the bottom of the fluid line. When
axial.
compressed air starts flowing, rising bubbles trans-
. What type of pump may be appropriate for pumping
port slugs of fluid upward. The process is enhanced
liquids near saturation, low flow rates and very limited
by the fact that bubbles also expand as they rise
NPSH A ?
because the hydrostatic head is decreasing.
& Regenerative turbine pump. The regenerative turbine
& When used for agitating a stratified tank, the fluid
is specifically developedfor these conditions and also
pipe should be completely submerged to move ma-
high discharge pressures. The regenerative turbine
terial from the lower parts of the vessel to the upper
can give a NPSH R of 15 cm (0.5 ft) with ease. They
sections. When used to lift fluid above its normal
are particularly suited to saturated boiler feed water.
surface, the fluid pipe should be submerged only
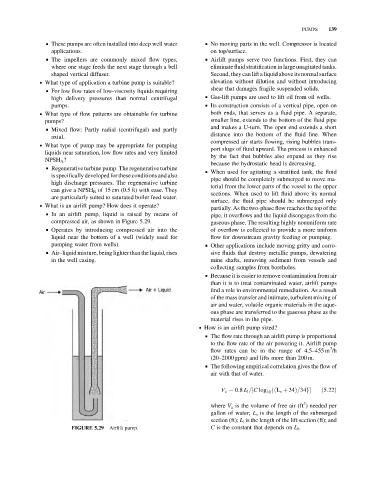
. What is an airlift pump? How does it operate?
partially. As the two-phase flow reaches the top of the
& In an airlift pump, liquid is raised by means of pipe, it overflows and the liquid disengages from the
compressed air, as shown in Figure 5.29. gaseous phase. The resulting highly nonuniform rate
& Operates by introducing compressed air into the of overflow is collected to provide a more uniform
liquid near the bottom of a well (widely used for flow for downstream gravity feeding or pumping.
pumping water from wells). & Other applications include moving gritty and corro-
& Air–liquid mixture, being lighter than the liquid, rises sive fluids that destroy metallic pumps, dewatering
in the well casing. mine shafts, removing sediment from vessels and
collecting samples from boreholes.
& Because it is easier to remove contamination from air
than it is to treat contaminated water, airlift pumps
find a role in environmental remediation. As a result
of the mass transfer and intimate, turbulent mixing of
air and water, volatile organic materials in the aque-
ous phase are transferred to the gaseous phase as the
material rises in the pipe.
. How is an airlift pump sized?
& The flow rate through an airlift pump is proportional
to the flow rate of the air powering it. Airlift pump
3
flow rates can be in the range of 4.5–455 m /h
(20–2000 gpm) and lifts more than 200 m.
& The following empirical correlation gives the flow of
air with that of water.
V a ¼ 0:8 L l =½C log fðL s þ 34Þ=34g ð5:22Þ
10
3
where V a is the volume of free air (ft ) needed per
gallon of water; L s is the length of the submerged
section (ft); L l is the length of the lift section (ft); and
FIGURE 5.29 Airlift pump. C is the constant that depends on L l .