Page 158 - Fluid mechanics, heat transfer, and mass transfer
P. 158
136 PUMPS, EJECTORS, BLOWERS, AND COMPRESSORS
& These are used for liquids with delicate suspended
solids requiring minimum damage. Examples in-
clude jams with fruit pieces, sausage meat filling,
pet foods, soups, and sausages containing solids.
& These pumps are used as boosters in series with a
vacuum pump, discharging gases to the vacuum
pump. The booster traps a pocket of gas and transfers
it from low pressure to higher pressure, limited to less
than about 100 Torr.
. Name the important criteria to be considered for desir-
able optimum conditions for lobe pumps handling
solids in suspension.
& Desirable properties of solids and operating
characteristics:
➢ Spherical and soft solid particles possessing resil-
ience and shear strength. Small solid concentra-
tions in the liquid.
➢ Smooth solid surfaces.
➢ Flow velocities sufficient to keep solids in suspen-
sion but not damage them. For example, while
pumping yeast, yoghurt, and other food products,
cell structure can be damaged if velocities are
high.
➢ Bilobe pumps are suited for the above
applications.
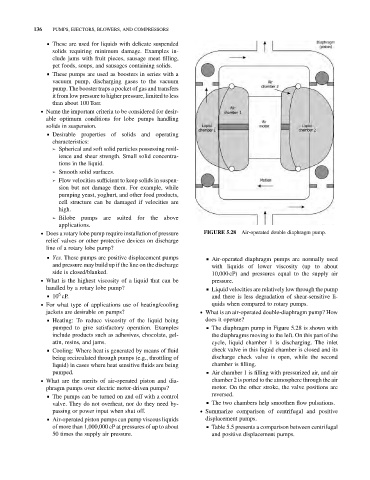
. Does a rotary lobe pump require installation of pressure FIGURE 5.28 Air-operated double diaphragm pump.
relief valves or other protective devices on discharge
line of a rotary lobe pump?
& Yes. These pumps are positive displacement pumps
& Air-operated diaphragm pumps are normally used
and pressure may build up if the line on the discharge with liquids of lower viscosity (up to about
side is closed/blanked. 10,000 cP) and pressures equal to the supply air
. What is the highest viscosity of a liquid that can be pressure.
handled by a rotary lobe pump? & Liquid velocities are relatively low through the pump
6
& 10 cP. and there is less degradation of shear-sensitive li-
. For what type of applications use of heating/cooling quids when compared to rotary pumps.
jackets are desirable on pumps? . What is an air-operated double-diaphragm pump? How
& Heating: To reduce viscosity of the liquid being does it operate?
pumped to give satisfactory operation. Examples & The diaphragm pump in Figure 5.28 is shown with
include products such as adhesives, chocolate, gel- the diaphragms moving to the left. On this part of the
atin, resins, and jams. cycle, liquid chamber 1 is discharging. The inlet
& Cooling: Where heat is generated by means of fluid check valve in this liquid chamber is closed and its
being recirculated through pumps (e.g., throttling of discharge check valve is open, while the second
liquid) in cases where heat sensitive fluids are being chamber is filling.
pumped. & Air chamber 1 is filling with pressurized air, and air
. What are the merits of air-operated piston and dia- chamber 2 is ported to the atmosphere through the air
phragm pumps over electric motor-driven pumps? motor. On the other stroke, the valve positions are
reversed.
& The pumps can be turned on and off with a control
valve. They do not overheat, nor do they need by- & The two chambers help smoothen flow pulsations.
passing or power input when shut off. . Summarize comparison of centrifugal and positive
& Air-operated piston pumps can pump viscous liquids displacement pumps.
of more than 1,000,000 cP at pressures of up to about & Table 5.5 presents a comparison between centrifugal
50 times the supply air pressure. and positive displacement pumps.