Page 159 - Fluid mechanics, heat transfer, and mass transfer
P. 159
PUMPS 137
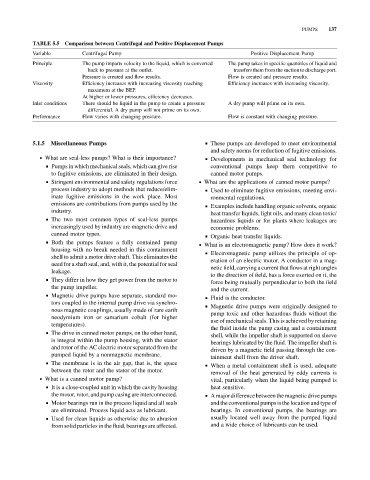
TABLE 5.5 Comparison between Centrifugal and Positive Displacement Pumps
Variable Centrifugal Pump Positive Displacement Pump
Principle The pump imparts velocity to the liquid, which is converted The pump takes in specific quantities of liquid and
back to pressure at the outlet. transfers them from the suction to discharge port.
Pressure is created and flow results. Flow is created and pressure results.
Viscosity Efficiency increases with increasing viscosity reaching Efficiency increases with increasing viscosity.
maximum at the BEP.
At higher or lower pressures, efficiency decreases.
Inlet conditions There should be liquid in the pump to create a pressure A dry pump will prime on its own.
differential. A dry pump will not prime on its own.
Performance Flow varies with changing pressure. Flow is constant with changing pressure.
5.1.5 Miscellaneous Pumps & These pumps are developed to meet environmental
and safety norms for reduction of fugitive emissions.
. What are seal-less pumps? What is their importance? & Developments in mechanical seal technology for
& Pumps in which mechanical seals, which can give rise conventional pumps keep them competitive to
to fugitive emissions, are eliminated in their design. canned motor pumps.
& Stringent environmental and safety regulations force . What are the applications of canned motor pumps?
process industry to adopt methods that reduce/elim- & Used to eliminate fugitive emissions, meeting envi-
inate fugitive emissions in the work place. Most ronmental regulations.
emissions are contributions from pumps used by the & Examples include handling organic solvents, organic
industry.
heat transfer liquids, light oils, and many clean toxic/
& The two most common types of seal-less pumps
hazardous liquids or for plants where leakages are
increasingly used by industry are magnetic drive and economic problems.
canned motor types. & Organic heat transfer liquids.
& Both the pumps feature a fully contained pump
. What is an electromagnetic pump? How does it work?
housing with no break needed in this containment
& Electromagnetic pump utilizes the principle of op-
shell to admit a motor drive shaft. This eliminates the
eration of an electric motor. A conductor in a mag-
need for a shaft seal, and, with it, the potential for seal
netic field, carrying a current that flows at right angles
leakage.
to the direction of field, has a force exerted on it, the
& They differ in how they get power from the motor to
force being mutually perpendicular to both the field
the pump impeller.
and the current.
& Magnetic drive pumps have separate, standard mo-
& Fluid is the conductor.
tors coupled to the internal pump drive via synchro-
& Magnetic drive pumps were originally designed to
nous magnetic couplings, usually made of rare earth
pump toxic and other hazardous fluids without the
neodymium iron or samarium cobalt (for higher
use of mechanical seals. This is achieved by retaining
temperatures).
the fluid inside the pump casing and a containment
& The drive in canned motor pumps, on the other hand,
shell, while the impeller shaft is supported on sleeve
is integral within the pump housing, with the stator
bearings lubricated by the fluid. The impeller shaft is
and rotor of the AC electric motor separated from the
driven by a magnetic field passing through the con-
pumped liquid by a nonmagnetic membrane.
tainment shell from the driver shaft.
& The membrane is in the air gap, that is, the space
& When a metal containment shell is used, adequate
between the rotor and the stator of the motor.
removal of the heat generated by eddy currents is
. What is a canned motor pump? vital, particularly when the liquid being pumped is
& It is a close-coupled unit in which the cavity housing heat sensitive.
the motor, rotor, and pump casing are interconnected. & Amajordifferencebetweenthemagneticdrivepumps
& Motor bearings run in the process liquid and all seals and the conventionalpumps is thelocation and type of
are eliminated. Process liquid acts as lubricant. bearings. In conventional pumps, the bearings are
& Used for clean liquids as otherwise due to abrasion usually located well away from the pumped liquid
from solid particles in the fluid, bearings are affected. and a wide choice of lubricants can be used.