Page 212 - Fluid mechanics, heat transfer, and mass transfer
P. 212
MIXING
190
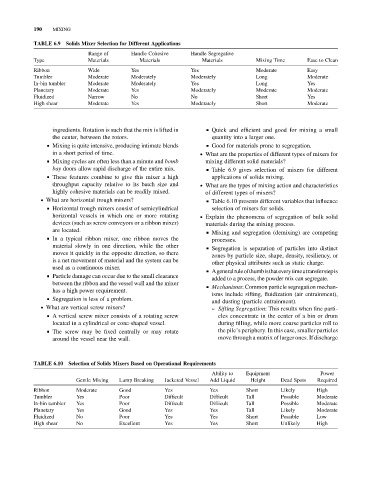
TABLE 6.9 Solids Mixer Selection for Different Applications
Range of Handle Cohesive Handle Segregative
Type Materials Materials Materials Mixing Time Ease to Clean
Ribbon Wide Yes Yes Moderate Easy
Tumbler Moderate Moderately Moderately Long Moderate
In-bin tumbler Moderate Moderately Yes Long Yes
Planetary Moderate Yes Moderately Moderate Moderate
Fluidized Narrow No No Short Yes
High shear Moderate Yes Moderately Short Moderate
ingredients. Rotation is such that the mix is lifted in & Quick and efficient and good for mixing a small
the center, between the rotors. quantity into a larger one.
& Mixing is quite intensive, producing intimate blends & Good for materials prone to segregation.
in a short period of time. . What are the properties of different types of mixers for
& Mixing cycles are often less than a minute and bomb mixing different solid materials?
bay doors allow rapid discharge of the entire mix. & Table 6.9 gives selection of mixers for different
& These features combine to give this mixer a high applications of solids mixing.
throughput capacity relative to its batch size and . What are the types of mixing action and characteristics
highly cohesive materials can be readily mixed. of different types of mixers?
. What are horizontal trough mixers? & Table 6.10 presents different variables that influence
& Horizontal trough mixers consist of semicylindrical selection of mixers for solids.
horizontal vessels in which one or more rotating . Explain the phenomena of segregation of bulk solid
devices (such as screw conveyors or a ribbon mixer) materials during the mixing process.
are located. & Mixing and segregation (demixing) are competing
& In a typical ribbon mixer, one ribbon moves the
processes.
material slowly in one direction, while the other & Segregation is separation of particles into distinct
moves it quickly in the opposite direction, so there
zones by particle size, shape, density, resiliency, or
is a net movement of material and the system can be
other physical attributes such as static charge.
used as a continuous mixer.
& Ageneralruleofthumbisthateverytimeatransferstepis
& Particle damage can occur due to the small clearance
added to a process, the powder mix can segregate.
between the ribbon and the vessel wall and the mixer
& Mechanisms: Common particle segregation mechan-
has a high power requirement.
isms include sifting, fluidization (air entrainment),
& Segregation is less of a problem.
and dusting (particle entrainment).
. What are vertical screw mixers? ➢ Sifting Segregation: This results when fine parti-
& A vertical screw mixer consists of a rotating screw cles concentrate in the center of a bin or drum
located in a cylindrical or cone-shaped vessel. during filling, while more coarse particles roll to
& The screw may be fixed centrally or may rotate the pile’s periphery. In this case, smaller particles
around the vessel near the wall. move through a matrix of larger ones. If discharge
TABLE 6.10 Selection of Solids Mixers Based on Operational Requirements
Ability to Equipment Power
Gentle Mixing Lump Breaking Jacketed Vessel Add Liquid Height Dead Spots Required
Ribbon Moderate Good Yes Yes Short Likely High
Tumbler Yes Poor Difficult Difficult Tall Possible Moderate
In-bin tumbler Yes Poor Difficult Difficult Tall Possible Moderate
Planetary Yes Good Yes Yes Tall Likely Moderate
Fluidized No Poor Yes Yes Short Possible Low
High shear No Excellent Yes Yes Short Unlikely High