Page 210 - Fluid mechanics, heat transfer, and mass transfer
P. 210
MIXING
188
& There are four main types of mixing equipment, convective and diffusive mechanisms of mixing, and
namely, tumbler, convective, hopper, and gentle mixing for friable particles. This type of
fluidization. rotating mixer comes in double cone or V-shaped
. What are tumbler mixers? What are their configurations, and in some cases, these geometries
characteristics? are given asymmetric features to reduce mix times
& Tumbler mixers operate by tumbling the solids inside and improve mix uniformity.
a revolving vessel. & Operate at speeds up to about 100 rpm (about half the
critical speed, at which the centrifugal force on the
& May be fitted with baffles to assist mixing or with
particles exceeds the pull of gravity).
internal rotating devices to break up agglomerates.
➢ Rotational speed is generally not as important of a
& The tumbler mixer is a mainstay in the pharmaceu-
factor in achieving uniformity as loading method
tical and food industries because of its features of
and mix time, based on the number of rotations.
close quality control in batch operation, effective
& Working capacity is about 50–60% of volume. Ca-
pacities are in the range of 0.014–5.66 m 3
3
(0.5–200 ft ).
& Best suited for gentle blending of particles with
similar physical characteristics; segregation can be
a problem.
& Equilibrium is generally reached in about 10–15 min.
& Typically, a top-to-bottom component loading is
better than a side-to-side loading with tumbler
mixers.
➢ With top-to-bottom loading, ingredients are al-
lowed to cascade into one another with diffusive
effects occurring perpendicular to the main flow.
This approach yields far faster mixing times than
side-to-side loading, whereby diffusive mixing
paces, and greatly increases, the mixing time.
➢ It is also important to avoid ingredient adherence
to the walls of the mixer. This is common with fine
additives, such as pigments and fumed silica, and
component loss can occur if the material does not
leave the wall surface.
➢ In some cases, the sticky ingredient can be pre-
mixed into another component, a practice known
as master batching, to help predisperse the mate-
rial and prevent wall adherence.
➢ Mix cohesiveness, which directly correlates to the
tendency of a material to form a bridge over the
outlet of the mixer, must also be considered.
➢ Highly cohesive blends should not be handled in
tumbler mixers if bridging or rat holing flow
obstructions have been experienced in past pro-
cessing equipment.
➢ To reduce mixing process bottlenecks and segrega-
tion potential, tumbling in-bin mixers have been
developed where the storage container, called an
intermediate bulk container, itself becomes a mixer.
➢ Mix components can be loaded into the container,
mixed, and transferred in the container to the point
of use or to a storage area.
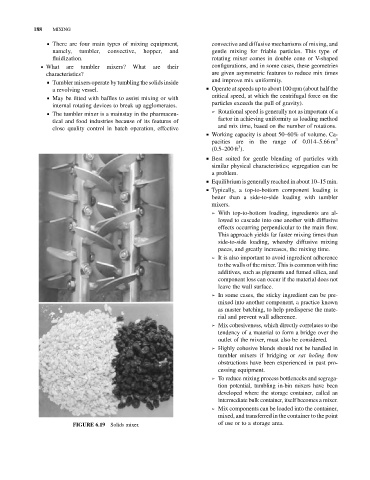
Solids mixer.
FIGURE 6.19