Page 209 - Fluid mechanics, heat transfer, and mass transfer
P. 209
MIXING EQUIPMENT 187
. What are the mechanisms of particulate mixing? What & A mix of perfect superparticles of identical size will
are mix structures? not segregate after discharge from the mixer, which is
clearly an advantage over a random mix.
& The three primary mechanisms of mixing are con-
vection, diffusion, and shear. & However, if these particles are not monosized, then
➢ Convective mixing involves gross movement of segregation by size may occur and induce problems
particles through the mixer, either by a force action with bulk density, reactivity, or solubility in postmix
from a paddle or by gentle cascading or tumbling processing.
under rotational effects. & With regard to mix structure, there are cases where
➢ Diffusion is a slow mixing mechanism and will some ingredients have a tendency to adhere only to
pace a mixing process in certain tumbler mixers if themselves, without adhering to dissimilar ingredi-
proper equipment fill order and method are not ents. This often happens with fine materials, such as
utilized. fumed silica, titanium dioxide, and carbon black.
➢ The shear mechanism of mixing involves thorough & Sometimes, a mix can reach saturation, where minor
incorporation of material passing along high-in- fine components will no longer coat larger particles
tensity, forced slip planes in a mixer. Often, these and concentrations of the fine component will build
mixers will infuse a liquid or powdered binder into and segregate from the mix.
the mix components to achieve a special consis- . Name and illustrate, with suitable diagrams, some
tency, such as granulates. commonly used mixers for solids mixing.
& There are two types of mix structures, namely, ran- & Ribbon blenders and double cone mixers are typical
dom and ordered. examples of mixers used for solids mixing.
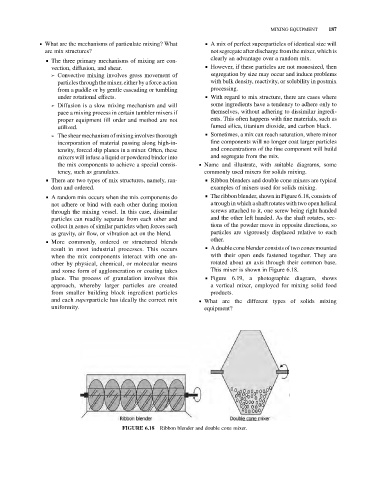
& A random mix occurs when the mix components do & The ribbon blender, shown in Figure 6.18, consists of
not adhere or bind with each other during motion a trough in which a shaft rotates with two open helical
through the mixing vessel. In this case, dissimilar screws attached to it, one screw being right handed
particles can readily separate from each other and and the other left handed. As the shaft rotates, sec-
collect in zones of similar particles when forces such tions of the powder move in opposite directions, so
as gravity, air flow, or vibration act on the blend. particles are vigorously displaced relative to each
& More commonly, ordered or structured blends other.
result in most industrial processes. This occurs & A double cone blender consists of two cones mounted
when the mix components interact with one an- with their open ends fastened together. They are
other by physical, chemical, or molecular means rotated about an axis through their common base.
and some form of agglomeration or coating takes This mixer is shown in Figure 6.18.
place. The process of granulation involves this & Figure 6.19, a photographic diagram, shows
approach, whereby larger particles are created a vertical mixer, employed for mixing solid food
from smaller building block ingredient particles products.
and each superparticle has ideally the correct mix . What are the different types of solids mixing
uniformity. equipment?
Ribbon blender and double cone mixer.
FIGURE 6.18