Page 204 - Fluid mechanics, heat transfer, and mass transfer
P. 204
MIXING
182
FIGURE 6.12 Double arm kneader.
cross-sectional loading of the machine as the sub- . What are helical mixers? For what type of applications
merged blades converge within the mass. these are used?
& Ribbon-type screws allow product to be expressed & Helical mixers comprise a series of mixing elements
and introduce a degree of backmixing in the mixer. with the leading edge of one element being perpen-
& The two shafts might be oriented with the mixing dicular to the trailing edge of the previous. Each
blades in either an even-space mode or a close-space mixing element is a metal or polymeric ribbon with a
mode. Close spacing of the blades increases the 180 helical twist that measures approximately one
amount of shear imparted to the product. The align- and a half pipe diameters in length. The mixing
ment of the blades is usually set by the factory elements can be permanently mounted inside a tube
according to the degree of work input considered or removable so as to allow for frequent cleaning and
appropriate for the duty. inspection.
& The angle of the blades is set at around 70 to the shaft & The helical mixer is used primarily for laminar flow
for general use. Flatter blades are fitted for more operations. Applications for the helical mixerinclude
agitation and finer settings for dealing with difficult liquid–liquid and gas–liquid mixing. These mixers
flow materials. can be used for laminar, transitional, and turbulent
flow applications and are suitable for most blending
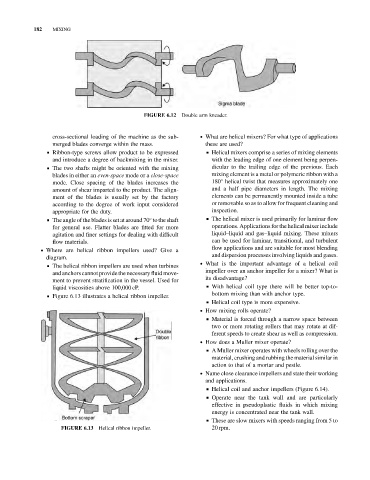
. Where are helical ribbon impellers used? Give a
and dispersion processes involving liquids and gases.
diagram.
. What is the important advantage of a helical coil
& The helical ribbon impellers are used when turbines
impeller over an anchor impeller for a mixer? What is
and anchors cannot providethe necessary fluid move-
its disadvantage?
ment to prevent stratification in the vessel. Used for
liquid viscosities above 100,000 cP. & With helical coil type there will be better top-to-
bottom mixing than with anchor type.
& Figure 6.13 illustrates a helical ribbon impeller.
& Helical coil type is more expensive.
. How mixing rolls operate?
& Material is forced through a narrow space between
two or more rotating rollers that may rotate at dif-
ferent speeds to create shear as well as compression.
. How does a Muller mixer operate?
& A Muller mixer operates with wheels rolling over the
material, crushing and rubbing the material similar in
action to that of a mortar and pestle.
. Name close clearance impellers and state their working
and applications.
& Helical coil and anchor impellers (Figure 6.14).
& Operate near the tank wall and are particularly
effective in pseudoplastic fluids in which mixing
energy is concentrated near the tank wall.
& These are slow mixers with speeds ranging from 5 to
Helical ribbon impeller. 20 rpm.
FIGURE 6.13