Page 201 - Fluid mechanics, heat transfer, and mass transfer
P. 201
MIXING EQUIPMENT 179
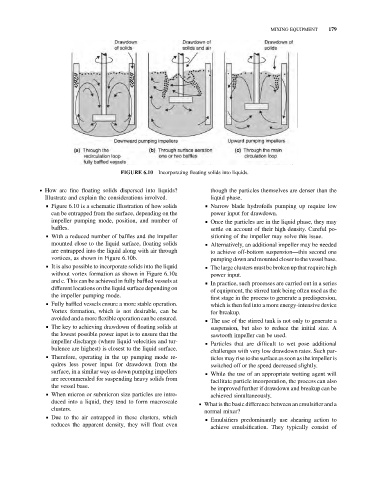
FIGURE 6.10 Incorporating floating solids into liquids.
. How are fine floating solids dispersed into liquids? though the particles themselves are denser than the
Illustrate and explain the considerations involved. liquid phase.
& Figure 6.10 is a schematic illustration of how solids & Narrow blade hydrofoils pumping up require low
can be entrapped from the surface, depending on the power input for drawdown.
impeller pumping mode, position, and number of & Once the particles are in the liquid phase, they may
baffles. settle on account of their high density. Careful po-
& With a reduced number of baffles and the impeller sitioning of the impeller may solve this issue.
mounted close to the liquid surface, floating solids & Alternatively, an additional impeller may be needed
are entrapped into the liquid along with air through to achieve off-bottom suspension—this second one
vortices, as shown in Figure 6.10b. pumping down and mounted closer to thevessel base.
& It is also possible to incorporate solids into the liquid & The large clusters must be broken up that require high
without vortex formation as shown in Figure 6.10a power input.
and c. This can be achieved in fully baffled vessels at & In practice, such processes are carried out in a series
different locations on the liquid surface depending on
of equipment, the stirred tank being often used as the
the impeller pumping mode.
first stage in the process to generate a predispersion,
& Fully baffled vessels ensure a more stable operation.
which is then fed into a more energy-intensive device
Vortex formation, which is not desirable, can be for breakup.
avoided and a more flexible operation can be ensured.
& The use of the stirred tank is not only to generate a
& The key to achieving drawdown of floating solids at suspension, but also to reduce the initial size. A
the lowest possible power input is to ensure that the sawtooth impeller can be used.
impeller discharge (where liquid velocities and tur- & Particles that are difficult to wet pose additional
bulence are highest) is closest to the liquid surface.
challenges with very low drawdown rates. Such par-
& Therefore, operating in the up pumping mode re-
ticles may rise to the surface as soon as the impeller is
quires less power input for drawdown from the switched off or the speed decreased slightly.
surface, in a similar way as down pumping impellers & While the use of an appropriate wetting agent will
are recommended for suspending heavy solids from
facilitate particle incorporation, the process can also
the vessel base.
be improved further if drawdown and breakup can be
& When micron or submicron size particles are intro-
achieved simultaneously.
duced into a liquid, they tend to form macroscale . What is the basic difference between an emulsifier and a
clusters.
normal mixer?
& Due to the air entrapped in these clusters, which
& Emulsifiers predominantly use shearing action to
reduces the apparent density, they will float even
achieve emulsification. They typically consist of