Page 273 - Forensic Structural Engineering Handbook
P. 273
DESIGN ERRORS, CONSTRUCTION DEFECTS, AND PROJECT MISCOMMUNICATION 8.13
South North
Roof
Seventh floor
Sixth floor
Fifth floor
Fourth floor
Third floor
Second floor
Finish
grade Upper level parking Column Beam
First floor
Lower level parking
Column
Foundation
Masonry Steel studs
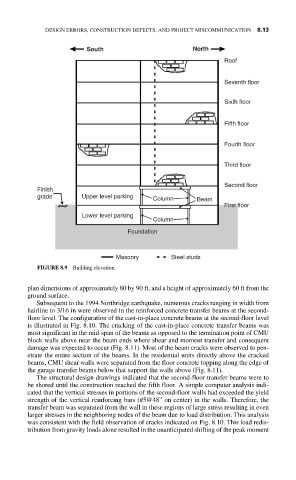
FIGURE 8.9 Building elevation.
plan dimensions of approximately 80 by 90 ft, and a height of approximately 60 ft from the
ground surface.
Subsequent to the 1994 Northridge earthquake, numerous cracks ranging in width from
hairline to 3/16 in were observed in the reinforced concrete transfer beams at the second-
floor level. The configuration of the cast-in-place concrete beams at the second-floor level
is illustrated in Fig. 8.10. The cracking of the cast-in-place concrete transfer beams was
most significant in the mid-span of the beams as opposed to the termination point of CMU
block walls above near the beam ends where shear and moment transfer and consequent
damage was expected to occur (Fig. 8.11). Most of the beam cracks were observed to pen-
etrate the entire section of the beams. In the residential units directly above the cracked
beams, CMU shear walls were separated from the floor concrete topping along the edge of
the garage transfer beams below that support the walls above (Fig. 8.11).
The structural design drawings indicated that the second-floor transfer beams were to
be shored until the construction reached the fifth floor. A simple computer analysis indi-
cated that the vertical stresses in portions of the second-floor walls had exceeded the yield
strength of the vertical reinforcing bars (#5@48” on center) in the walls. Therefore, the
transfer beam was separated from the wall in these regions of large stress resulting in even
larger stresses in the neighboring nodes of the beam due to load distribution. This analysis
was consistent with the field observation of cracks indicated on Fig. 8.10. This load redis-
tribution from gravity loads alone resulted in the unanticipated shifting of the peak moment