Page 365 - Subyek Teknik Mesin - Forsthoffers Best Practice Handbook for Rotating Machinery by William E Forsthoffer
P. 365
Be st Practice 6 .5 Gas Turbine Best Practices
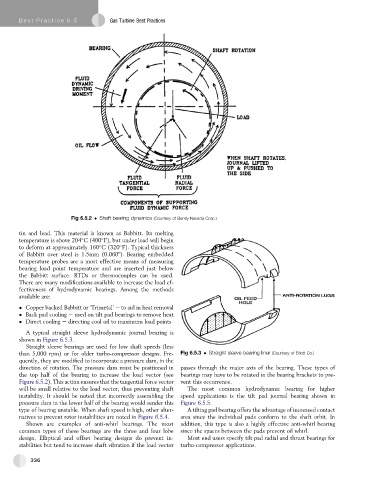
Fig 6.5.2 Shaft bearing dynamics (Courtesy of Bently Nevada Corp.)
tin and lead. This material is known as Babbitt. Its melting
temperature is above 204 C (400 F), but under load will begin
to deform at approximately 160 C (320 F). Typical thickness
of Babbitt over steel is 1.5mm (0.060"). Bearing embedded
temperature probes are a most effective means of measuring
bearing load point temperature and are inserted just below
the Babbitt surface. RTDs or thermocouples can be used.
There are many modifications available to increase the load ef-
fectiveness of hydrodynamic bearings. Among the methods
available are:
Copper backed Babbitt or ‘Trimetal’ e to aid in heat removal
Back pad cooling e used on tilt pad bearings to remove heat
Direct cooling e directing cool oil to maximum load points
A typical straight sleeve hydrodynamic journal bearing is
shown in Figure 6.5.3.
Straight sleeve bearings are used for low shaft speeds (less
than 5,000 rpm) or for older turbo-compressor designs. Fre- Fig 6.5.3 Straight sleeve bearing liner (Courtesy of Elliott Co.)
quently, they are modified to incorporate a pressure dam, in the
direction of rotation. The pressure dam must be positioned in passes through the major axis of the bearing. These types of
the top half of the bearing to increase the load vector (see bearings may have to be rotated in the bearing brackets to pre-
Figure 6.5.2). This action ensures that the tangential force vector vent this occurrence.
will be small relative to the load vector, thus preventing shaft The most common hydrodynamic bearing for higher
instability. It should be noted that incorrectly assembling the speed applications is the tilt pad journal bearing shown in
pressure dam in the lower half of the bearing would render this Figure 6.5.5.
type of bearing unstable. When shaft speed is high, other alter- A tilting pad bearing offers the advantage of increased contact
natives to prevent rotor instabilities are noted in Figure 6.5.4. area since the individual pads conform to the shaft orbit. In
Shown are examples of anti-whirl bearings. The most addition, this type is also a highly effective anti-whirl bearing
common types of these bearings are the three and four lobe since the spaces between the pads prevent oil whirl.
design. Elliptical and offset bearing designs do prevent in- Most end users specify tilt pad radial and thrust bearings for
stabilities but tend to increase shaft vibration if the load vector turbo-compressor applications.
336