Page 27 - From Smart Grid to Internet of Energy
P. 27
18 From smart grid to internet of energy
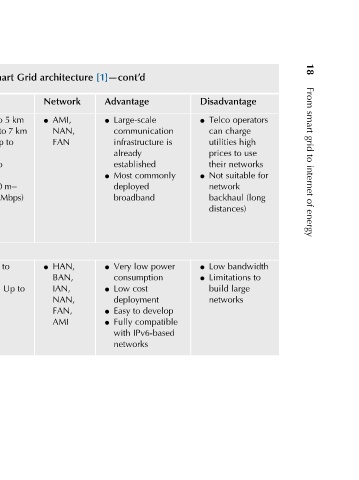
Disadvantage operators Telco l charge can high utilities use to prices networks their for suitable Not l network (long backhaul distances) bandwidth Low l to Limitations l large build networks
[1]—cont’d Advantage Large-scale l communication is infrastructure already established commonly Most l deployed broadband power low Very l consumption cost Low l deployment develop to Easy l compatible Fully l IPv6-based with networks
architecture Network AMI, NAN, FAN HAN, BAN, IAN, NAN, FAN, AMI
Grid l km km l to
Smart 5 to to up to m– 300 (50 Mbps) to Up Up Pro:
in Distance up ADSL: ADSL2: up to 7 ADSL2+: 7km up VDSL: km VDSL2: Km ZigBee: 100 m ZigBee 1600 m
technologies l down/ l l up l 1.2 up l 1.5 l l
communication rate Data Mbps 8 ADSL: up Mbps 1.3 12 Mbps ADSL2: Mbps down/3.5 24 Mbps ADSL2+: Mbps down/3.3 52–85 Mbps VDSL: down/16–85 Mbps up to up VDSL2: down/up 200 Mbps 802.15.4: IEEE 256 Kbps
wireless l l l l l l
and G.991.1 G.992.1 ITU (ADSL2), G.992.5 G.993.1 ITU (VDSL2) 802.15.4 ZigBee 100.11a 802.15.4)
Wireline Standard ITU (HDSL) ITU (ADSL), G.992.3 ITU (ADSL2+) ITU (VDSL), G.993.1 technologies IEEE ZigBee, ISA Pro, (IEEE
1.3 l l l l l
TABLE Tech. DSL Wireless WPAN