Page 25 - From Smart Grid to Internet of Energy
P. 25
Introduction to smart grid and internet of energy systems Chapter 1 17
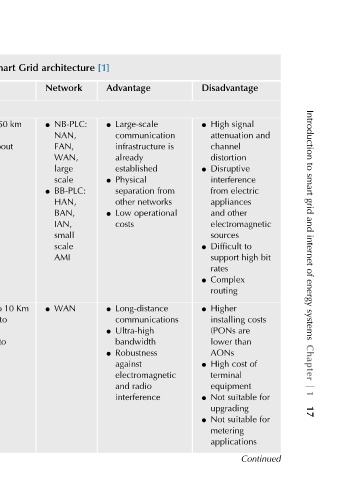
and to bit high costs of for for Continued
Disadvantage signal High l attenuation channel distortion Disruptive l interference electric from appliances other and electromagnetic sources Difficult l support rates Complex l routing Higher l installing are (PONs than lower AONs cost High l terminal equipment suitable Not l upgradin
Advantage Large-scale communication is infrastructure already established Physical from separation networks other operational Low costs Long-distance communications Ultra-high bandwidth Robustness against electromagnetic radio and interference
[1] l l l l l l
architecture Network NB-PLC: NAN, FAN, WAN, large scale BB-PLC: HAN, BAN, IAN, small scale AMI WAN
Grid l km l l
Smart 150 about to 10 Km to up to
in Distance NB-PLC: more BB-PLC: 1.5 km AON: up BPON: 20–60 Km up EPON: 20 Km
technologies l or l Kbps on l up/ l l up/
communication rate 1–10 Kbps NB-PLC: rate data low for 10–500 PHYs, data-rate high for PHYs 1–10 Mbps BB-PLC: 200 Mbps to (up distance) short very AON:100 Mbps down BPON:155– 622 Mbps 155– GPON: up, 2448 Mbps 1.244–2.448 Gbps down Gbps 1 EPON: down
wireless Data l IEC l l l l l
and ISO/IEC 14908–314,543– CEA-600.31, IEC61334–3-1, (FSK) TIA-1113 1.0), ITU- 1901, (G.9960/ HomePlug AV/Ext., Green HD-PLC (IEEE (ITU-T (ITU-T (IEEE
Wireline Standard technologies NB-PLC: 3-5, 61334–5 BB-PLC: (HomePlug IEEE G.hn T G.9961) BB-PLC: HomePlug PHY, AON 802.3ah) BPON G.983) GPON G.984) EPON 802.3ah)
1.3 l l l l l l l
TABLE Tech. Wireline PLC Fiber optic