Page 20 - From Smart Grid to Internet of Energy
P. 20
14 From smart grid to internet of energy
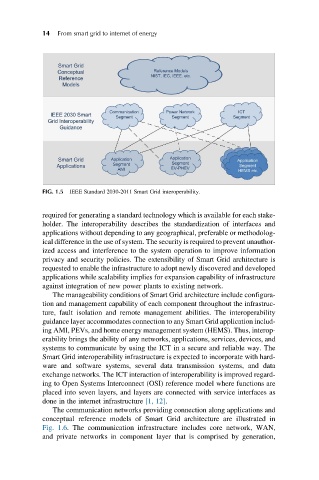
FIG. 1.5 IEEE Standard 2030-2011 Smart Grid interoperability.
required for generating a standard technology which is available for each stake-
holder. The interoperability describes the standardization of interfaces and
applications without depending to any geographical, preferable or methodolog-
ical difference in the use of system. The security is required to prevent unauthor-
ized access and interference to the system operation to improve information
privacy and security policies. The extensibility of Smart Grid architecture is
requested to enable the infrastructure to adopt newly discovered and developed
applications while scalability implies for expansion capability of infrastructure
against integration of new power plants to existing network.
The manageability conditions of Smart Grid architecture include configura-
tion and management capability of each component throughout the infrastruc-
ture, fault isolation and remote management abilities. The interoperability
guidance layer accommodates connection to any Smart Grid application includ-
ing AMI, PEVs, and home energy management system (HEMS). Thus, interop-
erability brings the ability of any networks, applications, services, devices, and
systems to communicate by using the ICT in a secure and reliable way. The
Smart Grid interoperability infrastructure is expected to incorporate with hard-
ware and software systems, several data transmission systems, and data
exchange networks. The ICT interaction of interoperability is improved regard-
ing to Open Systems Interconnect (OSI) reference model where functions are
placed into seven layers, and layers are connected with service interfaces as
done in the internet infrastructure [1, 12].
The communication networks providing connection along applications and
conceptual reference models of Smart Grid architecture are illustrated in
Fig. 1.6. The communication infrastructure includes core network, WAN,
and private networks in component layer that is comprised by generation,