Page 15 - From Smart Grid to Internet of Energy
P. 15
Introduction to smart grid and internet of energy systems Chapter 1 9
model describe the infrastructure including devices, systems and operation
software to manage the whole system. On the other hand, the operations are per-
formed by one or more shareholders in any domain division. The remote mon-
itoring, smart metering, energy generation with distributed sources and RESs,
energy storage and management are assumed as the operations and applications
in the conceptual model. The shareholders and actors in the same domain sys-
tems are responsible for similar objectives. The bulk generation, transmission,
distribution, and consumer domains are connected with power and communica-
tion networks while the other domains are interconnected by using only com-
munication flow that is based on two-way signal flow [9].
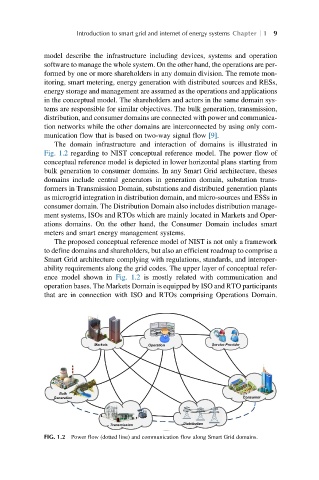
The domain infrastructure and interaction of domains is illustrated in
Fig. 1.2 regarding to NIST conceptual reference model. The power flow of
conceptual reference model is depicted in lower horizontal plans starting from
bulk generation to consumer domains. In any Smart Grid architecture, theses
domains include central generators in generation domain, substation trans-
formers in Transmission Domain, substations and distributed generation plants
as microgrid integration in distribution domain, and micro-sources and ESSs in
consumer domain. The Distribution Domain also includes distribution manage-
ment systems, ISOs and RTOs which are mainly located in Markets and Oper-
ations domains. On the other hand, the Consumer Domain includes smart
meters and smart energy management systems.
The proposed conceptual reference model of NIST is not only a framework
to define domains and shareholders, but also an efficient roadmap to comprise a
Smart Grid architecture complying with regulations, standards, and interoper-
ability requirements along the grid codes. The upper layer of conceptual refer-
ence model shown in Fig. 1.2 is mostly related with communication and
operation bases. The Markets Domain is equipped by ISO and RTO participants
that are in connection with ISO and RTOs comprising Operations Domain.
FIG. 1.2 Power flow (dotted line) and communication flow along Smart Grid domains.