Page 17 - From Smart Grid to Internet of Energy
P. 17
Introduction to smart grid and internet of energy systems Chapter 1 11
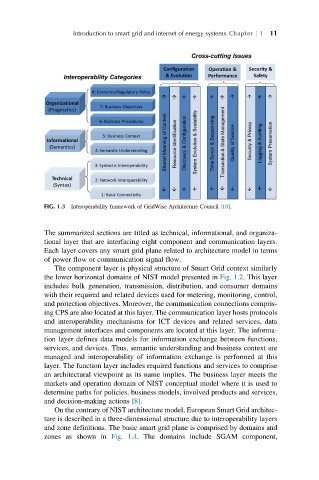
FIG. 1.3 Interoperability framework of GridWise Architecture Council [10].
The summarized sections are titled as technical, informational, and organiza-
tional layer that are interfacing eight component and communication layers.
Each layer covers any smart grid plane related to architecture model in terms
of power flow or communication signal flow.
The component layer is physical structure of Smart Grid context similarly
the lower horizontal domains of NIST model presented in Fig. 1.2. This layer
includes bulk generation, transmission, distribution, and consumer domains
with their required and related devices used for metering, monitoring, control,
and protection objectives. Moreover, the communication connections compris-
ing CPS are also located at this layer. The communication layer hosts protocols
and interoperability mechanisms for ICT devices and related services, data
management interfaces and components are located at this layer. The informa-
tion layer defines data models for information exchange between functions,
services, and devices. Thus, semantic understanding and business context are
managed and interoperability of information exchange is performed at this
layer. The function layer includes required functions and services to comprise
an architectural viewpoint as its name implies. The business layer meets the
markets and operation domain of NIST conceptual model where it is used to
determine paths for policies, business models, involved products and services,
and decision-making actions [8].
On the contrary of NIST architecture model, European Smart Grid architec-
ture is described in a three-dimensional structure due to interoperability layers
and zone definitions. The basic smart grid plane is comprised by domains and
zones as shown in Fig. 1.4. The domains include SGAM component,