Page 11 - From Smart Grid to Internet of Energy
P. 11
Introduction to smart grid and internet of energy systems Chapter 1 5
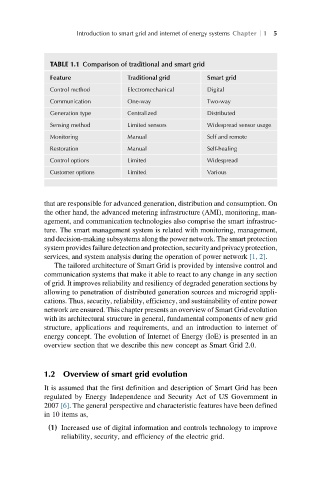
TABLE 1.1 Comparison of traditional and smart grid
Feature Traditional grid Smart grid
Control method Electromechanical Digital
Communication One-way Two-way
Generation type Centralized Distributed
Sensing method Limited sensors Widespread sensor usage
Monitoring Manual Self and remote
Restoration Manual Self-healing
Control options Limited Widespread
Customer options Limited Various
that are responsible for advanced generation, distribution and consumption. On
the other hand, the advanced metering infrastructure (AMI), monitoring, man-
agement, and communication technologies also comprise the smart infrastruc-
ture. The smart management system is related with monitoring, management,
and decision-making subsystems along the power network. The smart protection
systemprovides failuredetection andprotection,securityandprivacyprotection,
services, and system analysis during the operation of power network [1, 2].
The tailored architecture of Smart Grid is provided by intensive control and
communication systems that make it able to react to any change in any section
of grid. It improves reliability and resiliency of degraded generation sections by
allowing to penetration of distributed generation sources and microgrid appli-
cations. Thus, security, reliability, efficiency, and sustainability of entire power
network are ensured. This chapter presents an overview of Smart Grid evolution
with its architectural structure in general, fundamental components of new grid
structure, applications and requirements, and an introduction to internet of
energy concept. The evolution of Internet of Energy (IoE) is presented in an
overview section that we describe this new concept as Smart Grid 2.0.
1.2 Overview of smart grid evolution
It is assumed that the first definition and description of Smart Grid has been
regulated by Energy Independence and Security Act of US Government in
2007 [6]. The general perspective and characteristic features have been defined
in 10 items as,
(1) Increased use of digital information and controls technology to improve
reliability, security, and efficiency of the electric grid.