Page 28 - From Smart Grid to Internet of Energy
P. 28
costs
is
smart
to
management
consumption
requirement
devices
of
QoS
prices
service
equipment
Increased
cost
spectrum
Licensed
Complex
many
the
terminal
network
support
Simple
since
High
High
grid
use
for
l
l
l
l
l
l
oriented control of
QoS
cases
than
millions
distances
flexibility,
connection-
huge
simultaneous
sophisticated
use
mechanisms
channel
for
equipment
bandwidth
Wi-Fi
devices
of
Supports
Supports
802.11e
terminal
different
suitable
Longer
groups
More
users
High
than
the
of
A
l
l
l
l
l
l
WAN,
NAN,
HAN,
BAN,
FAN,
FAN,
FAN,
AMI
AMI
AMI
l
l
IEEE 802.16m: 0–5
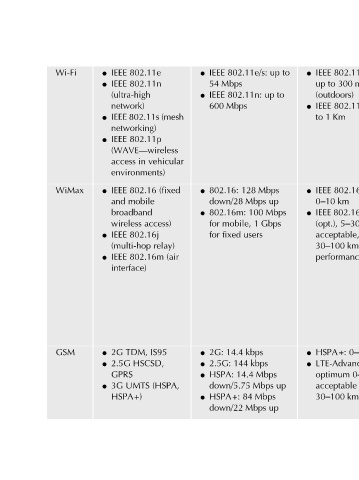
802.11e/s/n: High l network Low-cost l HAN, l interference deployments BAN, 300 m spectrum Cheaper l IAN, high-power Too l equipment NAN, up 802.11p: Introduction to smart grid and internet of energy systems Chapter provider power Low l IAN, km, 0–5 networks of consumption NAN, 5–30, 1 19 Continued
0–5km
low
LTE-Advanced:
802.16:
5–30
IEEE to up (outdoors) IEEE 1 Km to IEEE 0–10 km (opt.), acceptable, 30–100 km performance HSPA+: optimum acceptable 30–100 km
l l l l l l
to up
up to up up Mbps 1 Gbps up
802.11e/s: 802.11n: 128 Mbps down/28 Mbps 100 mobile, users fixed 14.4 kbps 144 kbps 14.4 Mbps down/5.75 Mbps 84 Mbps down/22 Mbps
IEEE 54 Mbps IEEE 600 Mbps 802.16: 802.16m: for for 2G: 2.5G: HSPA: HSPA+:
l l l l l l l l
802.11e 802.11n IEEE 802.11s (mesh networking) 802.11p (WAVE—wireless vehicular in environments) (fixed 802.16 mobile broadband access) 802.16j relay) (air 802.16m IS95 TDM, HSCSD, (HSPA, UMTS
IEEE IEEE (ultra-high network) IEEE access IEEE and wireless IEEE (multi-hop IEEE interface) 2G 2.5G GPRS 3G HSPA+)
l l l l l l l l l l
Wi-Fi WiMax GSM