Page 172 - Fundamentals of Communications Systems
P. 172
5.12 Chapter Five
After introducing the modulation and demodulation process students will
be motivated to learn about the trade-offs that various analog modulations
schemes offer for the final of the important performance metrics, fidelity.
Fidelity essentially reflects how the noise affects the various demodulation
processing and distorts the message reconstruction. So at that point the text
will return to the characterization of noise in communication systems and
eventually the characterization of the noise on analog communication system
performance.
5.5 Homework Problems
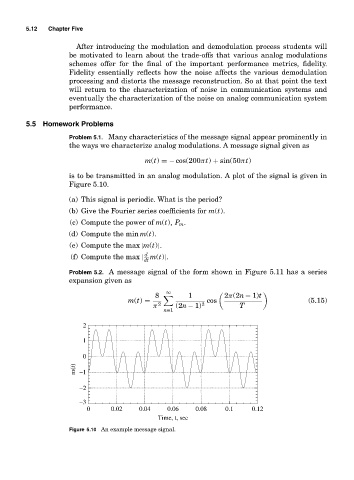
Problem 5.1. Many characteristics of the message signal appear prominently in
the ways we characterize analog modulations. A message signal given as
m(t) =− cos(200πt) + sin(50πt)
is to be transmitted in an analog modulation. A plot of the signal is given in
Figure 5.10.
(a) This signal is periodic. What is the period?
(b) Give the Fourier series coefficients for m(t).
(c) Compute the power of m(t), P m .
(d) Compute the min m(t).
(e) Compute the max |m(t)|.
d
(f) Compute the max | m(t)|.
dt
Problem 5.2. A message signal of the form shown in Figure 5.11 has a series
expansion given as
∞
8 1 2π(2n − 1)t
m(t) = cos (5.15)
π 2 (2n − 1) 2 T
n=1
2
1
0
m(t) −1
−2
−3
0 0.02 0.04 0.06 0.08 0.1 0.12
Time, t, sec
Figure 5.10 An example message signal.