Page 206 - Fundamentals of Communications Systems
P. 206
6.28 Chapter Six
(a) Give the baseband and bandpass forms of the modulated signal for this
message signal that has a power of8W(ina1 system).
(b) Assume f c = 10 f m give the baseband and bandpass spectral representa-
tion of this modulation. What is the transmission bandwidth, B T of such a
system?
(c) Plot the resulting bandpass signal for f m = 2 Hz.
(d) Give the simplest form of the modulator and demodulator (assume you
know φ p ).
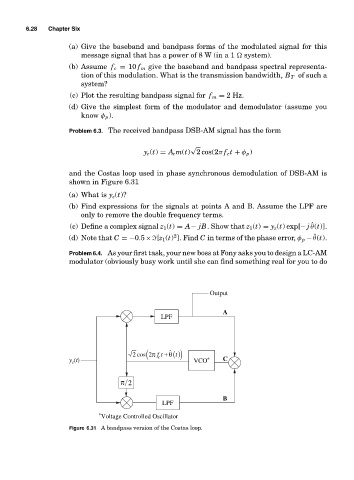
Problem 6.3. The received bandpass DSB-AM signal has the form
√
y c (t) = A c m(t) 2 cos(2π f c t + φ p )
and the Costas loop used in phase synchronous demodulation of DSB-AM is
shown in Figure 6.31
(a) What is y z (t)?
(b) Find expressions for the signals at points A and B. Assume the LPF are
only to remove the double frequency terms.
(c) Define a complex signal z 1 (t) = A− jB. Show that z 1 (t) = y z (t) exp[− j ˆ θ(t)].
2
(d) Note that C =−0.5× [z 1 (t) ]. Find C in terms of the phase error, φ p − ˆ θ(t).
Problem 6.4. As your first task, your new boss at Fony asks you to design a LC-AM
modulator (obviously busy work until she can find something real for you to do
Output
A
LPF
2 cos 2π f t +θ t ())
(
ˆ
y (t) c VCO ∗ C
c
π 2
B
LPF
∗ Voltage Controlled Oscillator
Figure 6.31 A bandpass version of the Costas loop.