Page 69 - Fundamentals of Communications Systems
P. 69
Signals and Systems Review 2.21
−40 −40
−45 −45
−50 −50
−55 −55
−60
G x (f), dB −60 G y (f) −65
−65
−70
−70
−75 −75
−80 −80
−85 −85
−90 −90
−5000 −3000 −1000 0 1000 3000 5000 −5000 −3000 −1000 0 1000 3000 5000
Frequency, f, Hz Frequency, f, Hz
(a) Input (b) Output
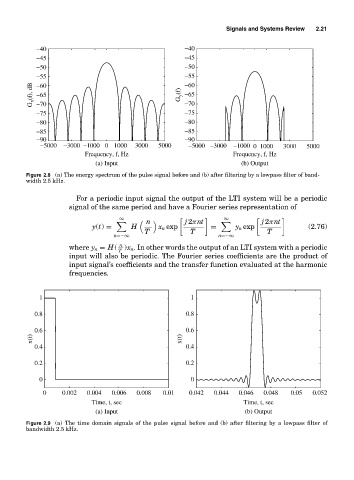
Figure 2.8 (a) The energy spectrum of the pulse signal before and (b) after filtering by a lowpass filter of band-
width 2.5 kHz.
For a periodic input signal the output of the LTI system will be a periodic
signal of the same period and have a Fourier series representation of
∞
∞
n j 2πnt j 2πnt
y(t) = H x n exp = y n exp (2.76)
T T T
n=−∞ n=−∞
where y n = H( n )x n . In other words the output of an LTI system with a periodic
T
input will also be periodic. The Fourier series coefficients are the product of
input signal’s coefficients and the transfer function evaluated at the harmonic
frequencies.
1 1
0.8 0.8
0.6 0.6
x(t) x(t)
0.4 0.4
0.2 0.2
0 0
0 0.002 0.004 0.006 0.008 0.01 0.042 0.044 0.046 0.048 0.05 0.052
Time, t, sec Time, t, sec
(a) Input (b) Output
Figure 2.9 (a) The time domain signals of the pulse signal before and (b) after filtering by a lowpass filter of
bandwidth 2.5 kHz.