Page 172 - Fundamentals of Gas Shale Reservoirs
P. 172
152 PORE PRESSuRE PREdIcTIOn FOR ShAlE FORmATIOnS uSInG WEll lOG dATA
Geralton
N
Bookara shelf
Irwin terrace
29 S Greenough shelf Bookara TF
Wlehe tine terrace
Allanooka TF
Basement
Darling fault
Abrolhos Dongara ridge
sub-basin Geraldton fault Abrolhor transfer fault Donkey creek Dandaragan trough
terrace
Deharra springer terrace
30 S Turtle dove ridge Beagle ridge Cadda terrace Coomallo fault Eneabba fault Yeara yarra terrace
Beagle fault system
Jurien
Maximum Coomallo fault Dandaragan trough
stress direction
Western Turtle dove transfer zone Cervantes transfer zone
Australia Beermullah trough Muchea fault
31 S Barberton terrace
0 50 km
115E 116E
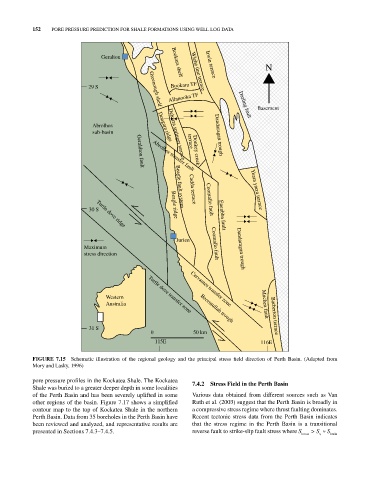
FIGURE 7.15 Schematic illustration of the regional geology and the principal stress field direction of Perth Basin. (Adapted from
mory and lasky, 1996)
pore pressure profiles in the Kockatea Shale. The Kockatea 7.4.2 Stress Field in the Perth basin
Shale was buried to a greater deeper depth in some localities
of the Perth Basin and has been severely uplifted in some Various data obtained from different sources such as Van
other regions of the basin. Figure 7.17 shows a simplified Ruth et al. (2003) suggest that the Perth Basin is broadly in
contour map to the top of Kockatea Shale in the northern a compressive stress regime where thrust faulting dominates.
Perth Basin. data from 35 boreholes in the Perth Basin have Recent tectonic stress data from the Perth Basin indicates
been reviewed and analyzed, and representative results are that the stress regime in the Perth Basin is a transitional
presented in Sections 7.4.3–7.4.5. reverse fault to strike‐slip fault stress where S > S ≈ S
hmax v hmin