Page 350 - Fundamentals of Gas Shale Reservoirs
P. 350
330 MOLECULAR SIMULATION OF GAS ADSORPTION IN MINERALS AND COAL
(a) (c)
2.0
0.90
Methane_O
Methane_Si
1.0 nm
1.5
Mole fraction of CH 4 adsorbed 0.80 2.0 nm RDF 1.0
Channel width: 10 Å
1.5 nm
0.85
0.5
0.0
0.75
mole fraction
CH 4
in bulk phase: 0.92 (d) 2.0 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
0.70 Ethane_O
0 3 6 9 12 15 Ethane_Si
(b) P (MPa) 1.5 Channel width: 10 Å
0.17
RDF 1.0
Mole fraction of C 2 H 6 adsorbed 0.14 1.0 nm (e) 0.0 2 3 4 5 Propane_O 8 9
0.16
H mole fraction
C 2 6
in bulk phase: 0.06
0.5
0.15
7
6
0.13
0.12
2.0
0.11
Propane_Si
2.0 nm
0.10
1.0
0.09 1.5 nm RDF 1.5 Channel width: 10 Å
0 3 6 9 12 15
P (MPa) 0.5
0.0
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
r (Å)
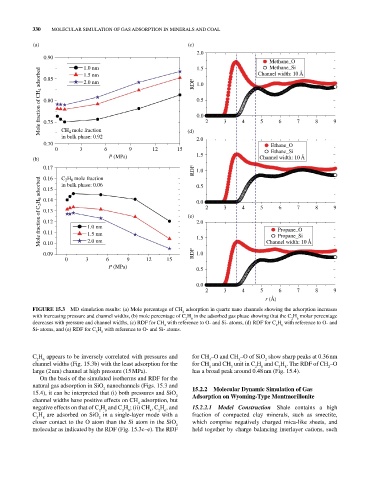
FIGURE 15.3 MD simulation results: (a) Mole percentage of CH adsorption in quartz nano channels showing the adsorption increases
4
with increasing pressure and channel widths, (b) mole percentage of C H in the adsorbed gas phase showing that the C H molar percentage
2
2
6
6
decreases with pressure and channel widths, (c) RDF for CH with reference to O‐ and Si‐ atoms, (d) RDF for C H with reference to O‐ and
2
4
6
Si‐ atoms, and (e) RDF for C H with reference to O‐ and Si‐ atoms.
3 8
C H appears to be inversely correlated with pressures and for CH –O and CH –O of SiO show sharp peaks at 0.36 nm
2
3
6
4
2
channel widths (Fig. 15.3b) with the least adsorption for the for CH and CH unit in C H and C H . The RDF of CH –O
4
8
2
2
6
3
3
large (2 nm) channel at high pressure (15 MPa). has a broad peak around 0.48 nm (Fig. 15.4).
On the basis of the simulated isotherms and RDF for the
natural gas adsorption in SiO nanochannels (Figs. 15.3 and 15.2.2 Molecular Dynamic Simulation of Gas
2
15.4), it can be interpreted that (i) both pressures and SiO Adsorption on Wyoming‐Type Montmorillonite
2
channel widths have positive effects on CH adsorption, but
4
negative effects on that of C H and C H ; (ii) CH , C H , and 15.2.2.1 Model Construction Shale contains a high
4
6
3
6
2
2
8
C H are adsorbed on SiO in a single‐layer mode with a fraction of compacted clay minerals, such as smectite,
3
8
2
closer contact to the O atom than the Si atom in the SiO which comprise negatively charged mica‐like sheets, and
2
molecular as indicated by the RDF (Fig. 15.3c–e). The RDF held together by charge balancing interlayer cations, such