Page 20 - Fundamentals of Light Microscopy and Electronic Imaging
P. 20
OPTICAL COMPONENTS OF THE LIGHT MICROSCOPE 3
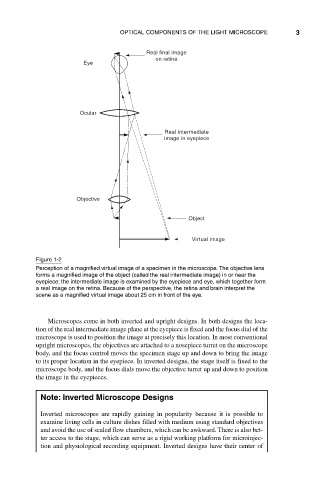
Real final image
on retina
Eye
Ocular
Real intermediate
image in eyepiece
Objective
Object
Virtual image
Figure 1-2
Perception of a magnified virtual image of a specimen in the microscope. The objective lens
forms a magnified image of the object (called the real intermediate image) in or near the
eyepiece; the intermediate image is examined by the eyepiece and eye, which together form
a real image on the retina. Because of the perspective, the retina and brain interpret the
scene as a magnified virtual image about 25 cm in front of the eye.
Microscopes come in both inverted and upright designs. In both designs the loca-
tion of the real intermediate image plane at the eyepiece is fixed and the focus dial of the
microscope is used to position the image at precisely this location. In most conventional
upright microscopes, the objectives are attached to a nosepiece turret on the microscope
body, and the focus control moves the specimen stage up and down to bring the image
to its proper location in the eyepiece. In inverted designs, the stage itself is fixed to the
microscope body, and the focus dials move the objective turret up and down to position
the image in the eyepieces.
Note: Inverted Microscope Designs
Inverted microscopes are rapidly gaining in popularity because it is possible to
examine living cells in culture dishes filled with medium using standard objectives
and avoid the use of sealed flow chambers, which can be awkward. There is also bet-
ter access to the stage, which can serve as a rigid working platform for microinjec-
tion and physiological recording equipment. Inverted designs have their center of