Page 382 - Fundamentals of Magnetic Thermonuclear Reactor Design
P. 382
360 Fundamentals of Magnetic Thermonuclear Reactor Design
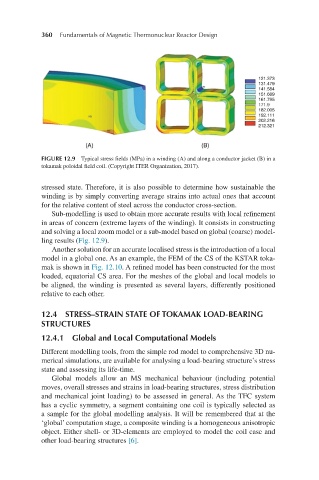
FIGURE 12.9 Typical stress fields (MPa) in a winding (A) and along a conductor jacket (B) in a
tokamak poloidal field coil. (Copyright ITER Organization, 2017).
stressed state. Therefore, it is also possible to determine how sustainable the
winding is by simply converting average strains into actual ones that account
for the relative content of steel across the conductor cross-section.
Sub-modelling is used to obtain more accurate results with local refinement
in areas of concern (extreme layers of the winding). It consists in constructing
and solving a local zoom model or a sub-model based on global (coarse) model-
ling results (Fig. 12.9).
Another solution for an accurate localised stress is the introduction of a local
model in a global one. As an example, the FEM of the CS of the KSTAR toka-
mak is shown in Fig. 12.10. A refined model has been constructed for the most
loaded, equatorial CS area. For the meshes of the global and local models to
be aligned, the winding is presented as several layers, differently positioned
relative to each other.
12.4 STRESS–STRAIN STATE OF TOKAMAK LOAD-BEARING
STRUCTURES
12.4.1 Global and Local Computational Models
Different modelling tools, from the simple rod model to comprehensive 3D nu-
merical simulations, are available for analysing a load-bearing structure’s stress
state and assessing its life-time.
Global models allow an MS mechanical behaviour (including potential
moves, overall stresses and strains in load-bearing structures, stress distribution
and mechanical joint loading) to be assessed in general. As the TFC system
has a cyclic symmetry, a segment containing one coil is typically selected as
a sample for the global modelling analysis. It will be remembered that at the
‘global’ computation stage, a composite winding is a homogeneous anisotropic
object. Either shell- or 3D-elements are employed to model the coil case and
other load-bearing structures [6].