Page 156 - Fundamentals of Probability and Statistics for Engineers
P. 156
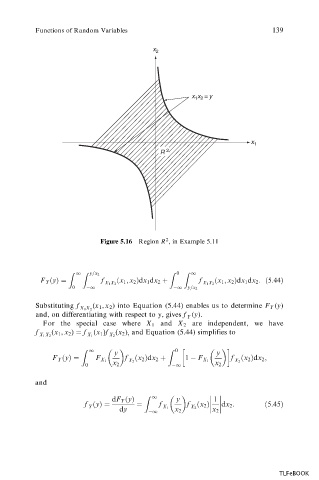
Functions of Random Variables 139
x
2
x x = y
1 2
x 1
R 2
2
Figure 5.16 Region R , in Example 5.11
Z 1 Z y=x 2 Z 0 Z 1
F Y
y f
x 1 ; x 2 dx 1 dx 2 f
x 1 ; x 2 dx 1 dx 2 :
5:44
X 1 X 2 X 1 X 2
0
1
1 y=x 2
Substituting f (x 1 , x 2 ) into Equation (5.44) enables us to determine F Y (y)
X 1 X 2
and, on differentiating with respect to y, gives f (y).
Y
For the special case where X 1 and X 2 are independent, we have
f x 1 , x 2 ) f x 1 )f x 2 ); and Equation (5.44) simplifies to
X 1 X 2 X 1 X 2
1 0
Z y Z y
F Y
y F X 1 f
x 2 dx 2 1
F X 1 f
x 2 dx 2 ;
X 2 X 2
0 x 2
1 x 2
and
y
dF Y
y Z 1
1
f
y f f
x 2 dx 2 :
5:45
Y
dy
1 X 1 x 2 X 2
x 2
TLFeBOOK