Page 70 - Fundamentals of Probability and Statistics for Engineers
P. 70
Random Variables and Probability Distributions 53
5
p XY
5; 0 p :
For p (4, 1), there are five distinct ways of reaching that position (4 steps in
XY
the x direction and 1 in y; 3 in the x direction, 1 in y, and 1 in the x direction;
4
and so on), each with a probability of p q. We thus have
4
p
4; 1 5p q:
XY
Similarly, other nonvanishing values of p XY (x, y) are easily calculated to be
8 3 2
10p q ; for
x; y
3; 2;
>
>
>
10p q ; for
x; y
2; 3;
< 2 3
p XY
x; y
4
5pq ; for
x; y
1; 4;
>
>
>
q ; for
x; y
0; 5:
: 5
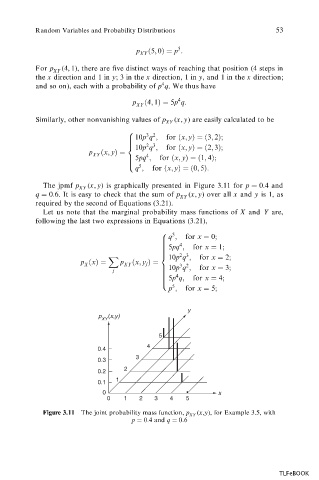
The jpmf p XY (x, y) is graphically presented in Figure 3.11 for p :
0 4 and
0 6. It is easy to check that the sum of p
q : (x, y) over all x and y is 1, as
XY
required by the second of Equations (3.21).
Let us note that the marginal probability mass functions of X and Y are,
following the last two expressions in Equations (3.21),
q ; for x 0;
8 5
>
>
5pq ; for x 1;
> 4
>
>
>
> 2 3
<
X 10p q ; for x 2;
p
x p XY
x; y j 3 2
X
j > 10p q ; for x 3;
>
>
> 4
> 5p q; for x 4;
>
>
: 5
p ; for x 5;
y
p (x,y)
XY
5
4
0.4
3
0.3
0.2 2
1
0.1
0 x
0 1 2 3 4 5
Figure 3.11 The joint probability mass function, p XY (x,y), for Example 3.5, with
p 0:4 and q 0:6
TLFeBOOK