Page 42 - Fundamentals of Radar Signal Processing
P. 42
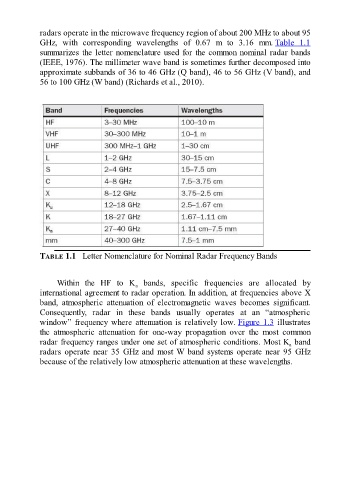
radars operate in the microwave frequency region of about 200 MHz to about 95
GHz, with corresponding wavelengths of 0.67 m to 3.16 mm. Table 1.1
summarizes the letter nomenclature used for the common nominal radar bands
(IEEE, 1976). The millimeter wave band is sometimes further decomposed into
approximate subbands of 36 to 46 GHz (Q band), 46 to 56 GHz (V band), and
56 to 100 GHz (W band) (Richards et al., 2010).
TABLE 1.1 Letter Nomenclature for Nominal Radar Frequency Bands
Within the HF to K bands, specific frequencies are allocated by
a
international agreement to radar operation. In addition, at frequencies above X
band, atmospheric attenuation of electromagnetic waves becomes significant.
Consequently, radar in these bands usually operates at an “atmospheric
window” frequency where attenuation is relatively low. Figure 1.3 illustrates
the atmospheric attenuation for one-way propagation over the most common
radar frequency ranges under one set of atmospheric conditions. Most K band
a
radars operate near 35 GHz and most W band systems operate near 95 GHz
because of the relatively low atmospheric attenuation at these wavelengths.