Page 44 - Fundamentals of Radar Signal Processing
P. 44
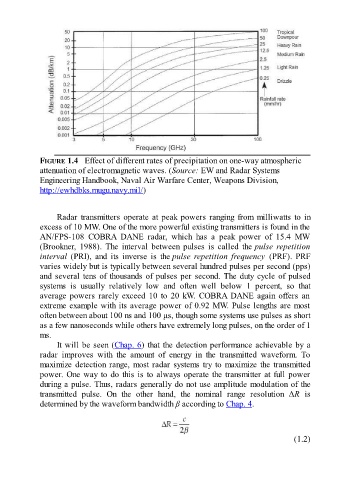
FIGURE 1.4 Effect of different rates of precipitation on one-way atmospheric
attenuation of electromagnetic waves. (Source: EW and Radar Systems
Engineering Handbook, Naval Air Warfare Center, Weapons Division,
http://ewhdbks.mugu.navy.mil/)
Radar transmitters operate at peak powers ranging from milliwatts to in
excess of 10 MW. One of the more powerful existing transmitters is found in the
AN/FPS-108 COBRA DANE radar, which has a peak power of 15.4 MW
(Brookner, 1988). The interval between pulses is called the pulse repetition
interval (PRI), and its inverse is the pulse repetition frequency (PRF). PRF
varies widely but is typically between several hundred pulses per second (pps)
and several tens of thousands of pulses per second. The duty cycle of pulsed
systems is usually relatively low and often well below 1 percent, so that
average powers rarely exceed 10 to 20 kW. COBRA DANE again offers an
extreme example with its average power of 0.92 MW. Pulse lengths are most
often between about 100 ns and 100 μs, though some systems use pulses as short
as a few nanoseconds while others have extremely long pulses, on the order of 1
ms.
It will be seen (Chap. 6) that the detection performance achievable by a
radar improves with the amount of energy in the transmitted waveform. To
maximize detection range, most radar systems try to maximize the transmitted
power. One way to do this is to always operate the transmitter at full power
during a pulse. Thus, radars generally do not use amplitude modulation of the
transmitted pulse. On the other hand, the nominal range resolution ΔR is
determined by the waveform bandwidth β according to Chap. 4.
(1.2)