Page 424 - Fundamentals of Radar Signal Processing
P. 424
combining samples staggered by this delay time from the slow-time data streams
from the same range bin but different receive subapertures, effective MTI
cancellation can be achieved. References for basic DPCA are Skolnik (2001),
Shaw and McAulay (1983), Staudaher (1990), and Lightstone et al. (1991).
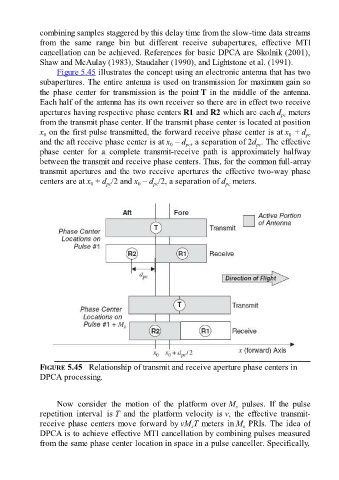
Figure 5.45 illustrates the concept using an electronic antenna that has two
subapertures. The entire antenna is used on transmission for maximum gain so
the phase center for transmission is the point T in the middle of the antenna.
Each half of the antenna has its own receiver so there are in effect two receive
apertures having respective phase centers R1 and R2 which are each d meters
pc
from the transmit phase center. If the transmit phase center is located at position
x on the first pulse transmitted, the forward receive phase center is at x + d pc
0
0
and the aft receive phase center is at x – d , a separation of 2d . The effective
0
pc
pc
phase center for a complete transmit-receive path is approximately halfway
between the transmit and receive phase centers. Thus, for the common full-array
transmit apertures and the two receive apertures the effective two-way phase
centers are at x + d /2 and x – d /2, a separation of d meters.
0
0
pc
pc
pc
FIGURE 5.45 Relationship of transmit and receive aperture phase centers in
DPCA processing.
Now consider the motion of the platform over M pulses. If the pulse
s
repetition interval is T and the platform velocity is v, the effective transmit-
receive phase centers move forward by vM T meters in M PRIs. The idea of
s
s
DPCA is to achieve effective MTI cancellation by combining pulses measured
from the same phase center location in space in a pulse canceller. Specifically,