Page 266 - Fundamentals of Reservoir Engineering
P. 266
OILWELL TESTING 203
Closed-in time Closed-in Closed-in time Closed-in
∆t (hrs) pressure p ws (psi) ∆t (hrs) pressure p ws (psi)
0 1889 6 2790
0.5 2683 7.5 2795
1 2713 10 2804
1.5 2743 12 2809
2 2752 14 2813
2.5 2760 16 2817
3 2766 20 2823
3.5 2771 25 2833
4 2777 30 2840
4.5 2779 36 2844
5 2783
TABLE 7.7
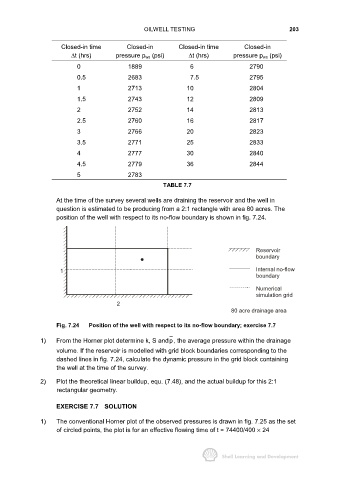
At the time of the survey several wells are draining the reservoir and the well in
question is estimated to be producing from a 2:1 rectangle with area 80 acres. The
position of the well with respect to its no-flow boundary is shown in fig. 7.24.
Reservoir
boundary
1 Internal no-flow
boundary
Numerical
simulation grid
2
80 acre drainage area
Fig. 7.24 Position of the well with respect to its no-flow boundary; exercise 7.7
1) From the Horner plot determine k, S andp, the average pressure within the drainage
volume. If the reservoir is modelled with grid block boundaries corresponding to the
dashed lines in fig. 7.24, calculate the dynamic pressure in the grid block containing
the well at the time of the survey.
2) Plot the theoretical linear buildup, equ. (7.48), and the actual buildup for this 2:1
rectangular geometry.
EXERCISE 7.7 SOLUTION
1) The conventional Horner plot of the observed pressures is drawn in fig. 7.25 as the set
of circled points, the plot is for an effective flowing time of t = 74400/400 × 24