Page 283 - Fundamentals of The Finite Element Method for Heat and Fluid Flow
P. 283
275
SOME EXAMPLES OF FLUID FLOW AND HEAT TRANSFER PROBLEMS
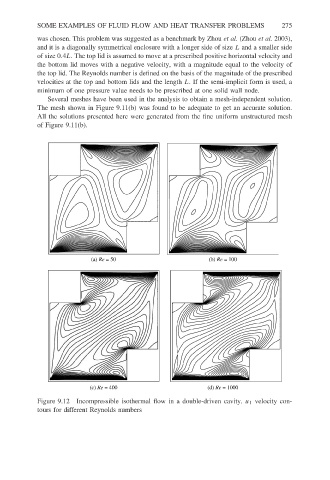
was chosen. This problem was suggested as a benchmark by Zhou et al. (Zhou et al. 2003),
and it is a diagonally symmetrical enclosure with a longer side of size L and a smaller side
of size 0.4L. The top lid is assumed to move at a prescribed positive horizontal velocity and
the bottom lid moves with a negative velocity, with a magnitude equal to the velocity of
the top lid. The Reynolds number is defined on the basis of the magnitude of the prescribed
velocities at the top and bottom lids and the length L. If the semi-implicit form is used, a
minimum of one pressure value needs to be prescribed at one solid wall node.
Several meshes have been used in the analysis to obtain a mesh-independent solution.
The mesh shown in Figure 9.11(b) was found to be adequate to get an accurate solution.
All the solutions presented here were generated from the fine uniform unstructured mesh
of Figure 9.11(b).
(a) Re = 50 (b) Re = 100
(c) Re = 400 (d) Re = 1000
Figure 9.12 Incompressible isothermal flow in a double-driven cavity. u 1 velocity con-
tours for different Reynolds numbers