Page 48 - Fundamentals of The Finite Element Method for Heat and Fluid Flow
P. 48
40
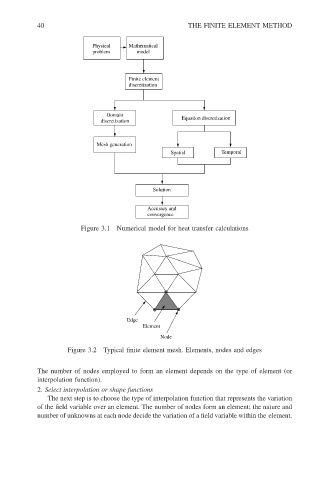
Physical
problem Mathematical THE FINITE ELEMENT METHOD
model
Finite element
discretization
Domain
discretization Equation discretization
Mesh generation
Spatial Temporal
Solution
Accuracy and
convergence
Figure 3.1 Numerical model for heat transfer calculations
Edge
Element
Node
Figure 3.2 Typical finite element mesh. Elements, nodes and edges
The number of nodes employed to form an element depends on the type of element (or
interpolation function).
2. Select interpolation or shape functions
The next step is to choose the type of interpolation function that represents the variation
of the field variable over an element. The number of nodes form an element; the nature and
number of unknowns at each node decide the variation of a field variable within the element.