Page 103 - Fundamentals of Water Treatment Unit Processes : Physical, Chemical, and Biological
P. 103
58 Fundamentals of Water Treatment Unit Processes: Physical, Chemical, and Biological
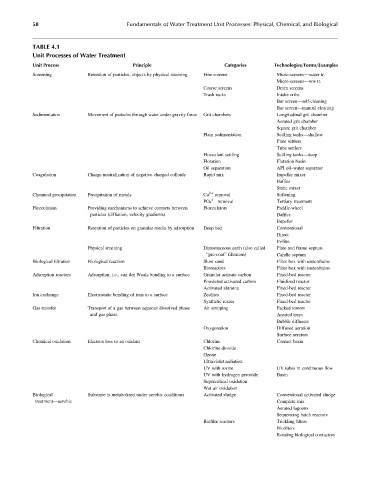
TABLE 4.1
Unit Processes of Water Treatment
Unit Process Principle Categories Technologies=Forms=Examples
Screening Retention of particles, objects by physical straining Fine screens Micro-screens—water tr.
Micro-screens—ww tr.
Coarse screens Drum screens
Trash racks Intake cribs
Bar screen—self-cleaning
Bar screen—manual cleaning
Sedimentation Movement of particles through water under gravity force Grit chambers Longitudinal grit chamber
Aerated grit chamber
Square grit chamber
Plain sedimentation Settling tanks—shallow
Plate settlers
Tube settlers
Flocculant settling Settling tanks—deep
Flotation Flotation basin
Oil separation API oil–water separator
Coagulation Charge neutralization of negative charged colloids Rapid mix Impeller mixer
Baffles
Static mixer
Chemical precipitation Precipitation of metals Ca 2þ removal Softening
3 removal Tertiary treatment
PO 4
Flocculation Providing mechanisms to achieve contacts between Flocculators Paddle-wheel
particles (diffusion, velocity gradients) Baffles
Impeller
Filtration Retention of particles on granular media by adsorption Deep bed Conventional
Direct
In-line
Physical straining Diatomaceous earth (also called Plate and frame septum
‘‘pre-coat’’ filtration) Candle septum
Biological filtration Biological reaction Slow sand Filter box with underdrains
Bioreactors Filter box with underdrains
Adsorption reactors Adsorption, i.e., van der Waals bonding to a surface Granular activate carbon Fixed-bed reactor
Powdered activated carbon Fluidized reactor
Activated alumina Fixed-bed reactor
Ion exchange Electrostatic bonding of ions to a surface Zeolites Fixed-bed reactor
Synthetic resins Fixed-bed reactor
Gas transfer Transport of a gas between aqueous dissolved phase Air stripping Packed towers
and gas phase Aerated trays
Bubble diffusers
Oxygenation Diffused aeration
Surface aerators
Chemical oxidation Electron loss to an oxidant Chlorine Contact basin
Chlorine dioxide
Ozone
Ultraviolet radiation
UV with ozone UV tubes in continuous flow
UV with hydrogen peroxide Basin
Supercritical oxidation
Wet air oxidation
Biological Substrate is metabolized under aerobic conditions Activated sludge Conventional activated sludge
treatment—aerobic Complete mix
Aerated lagoons
Sequencing batch reactors
Biofilm reactors Trickling filters
Biofilters
Rotating biological contactors